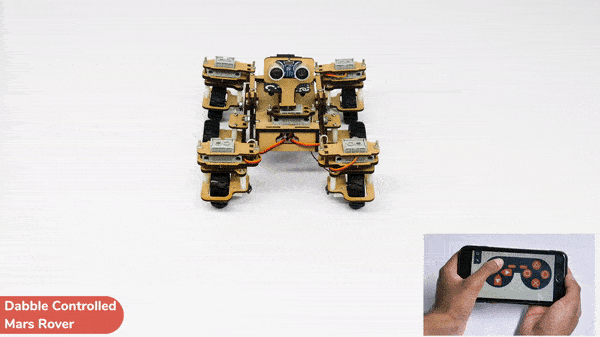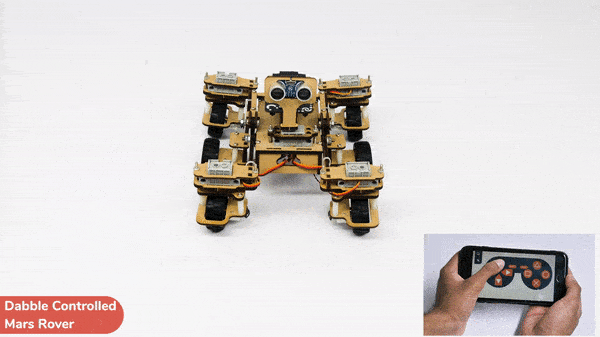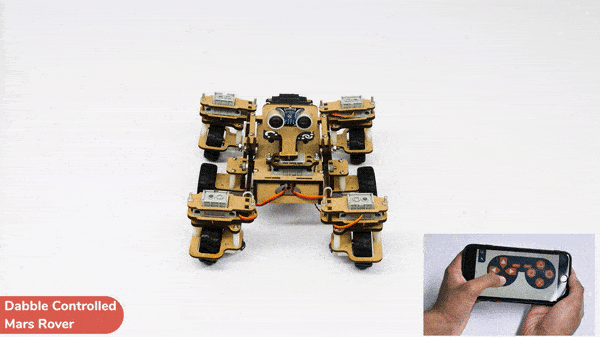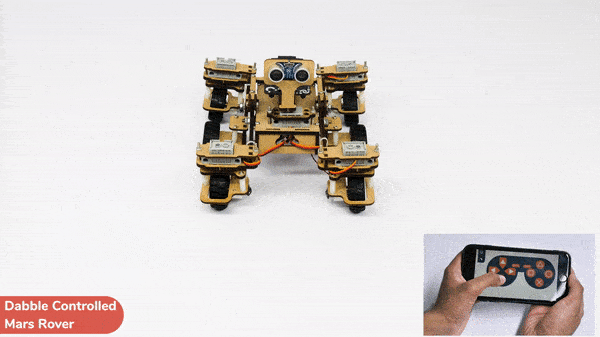
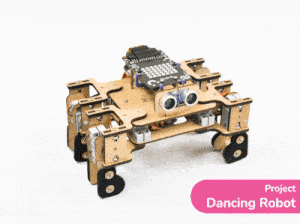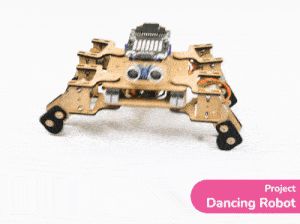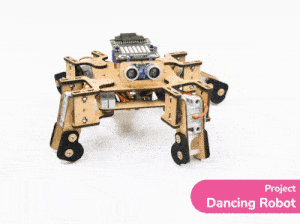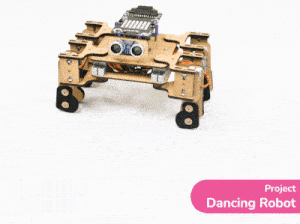
[PictoBloxExtension]
Quarky Mecanum
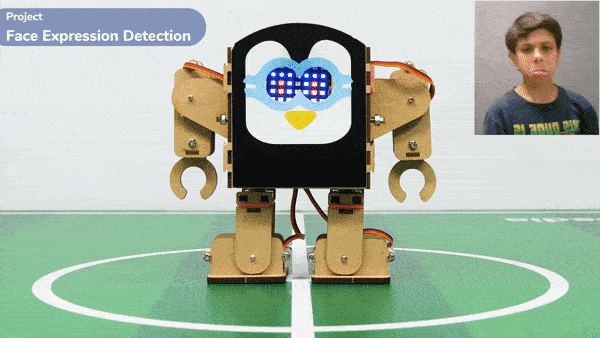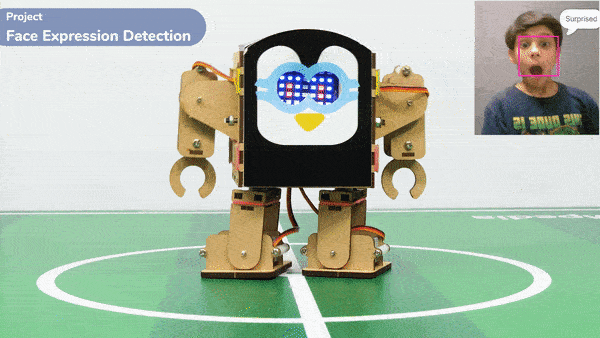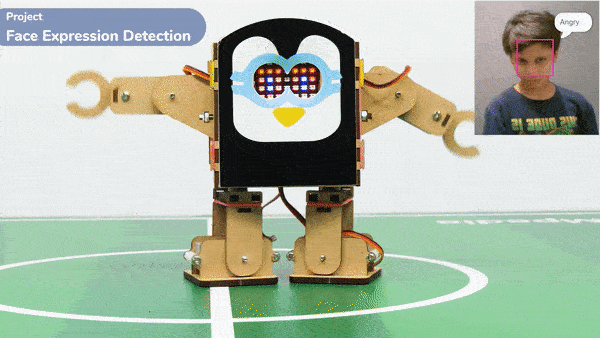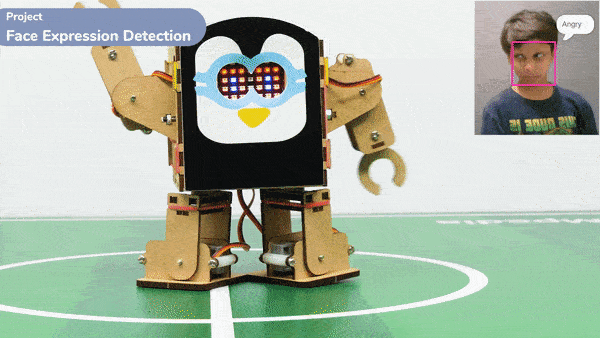
Extension Description
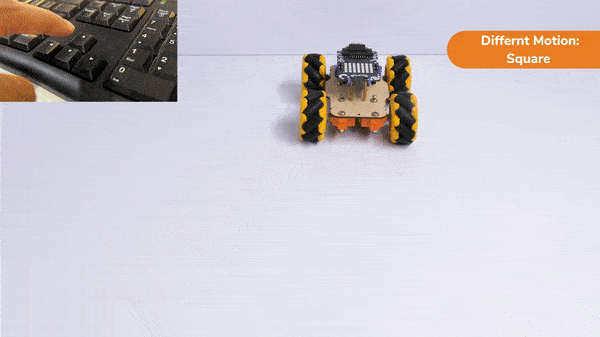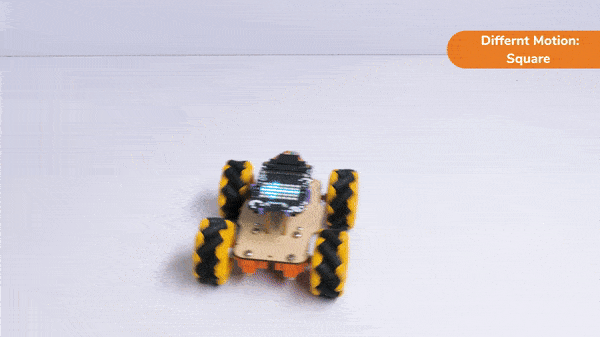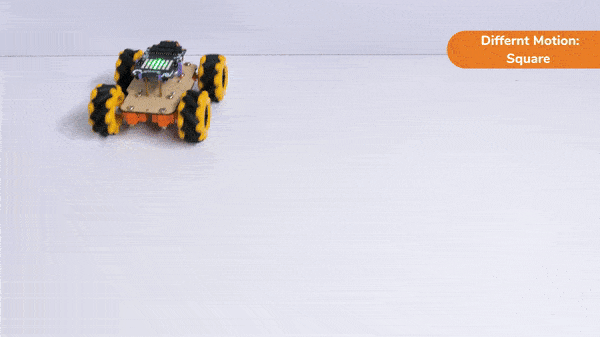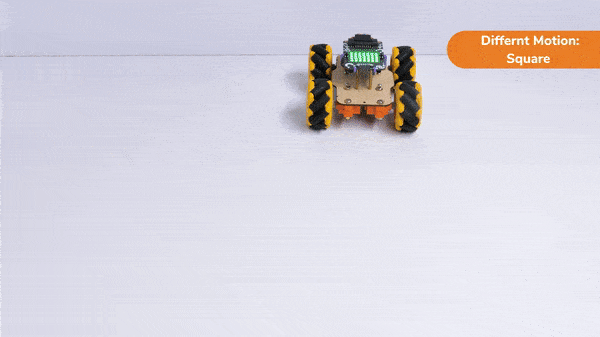
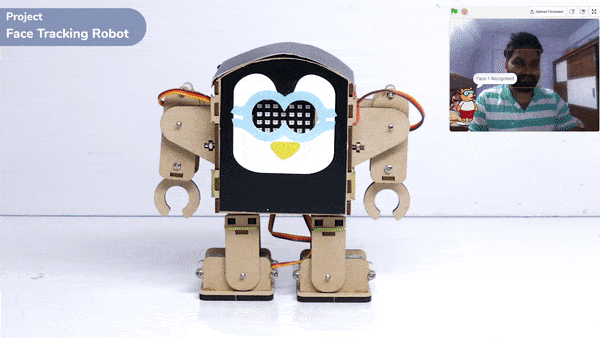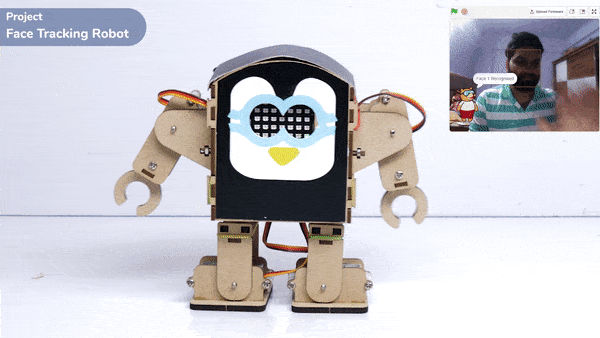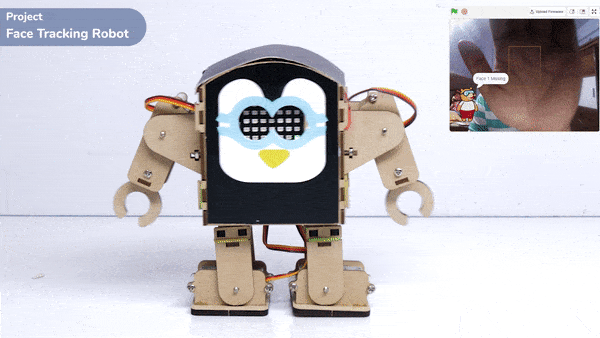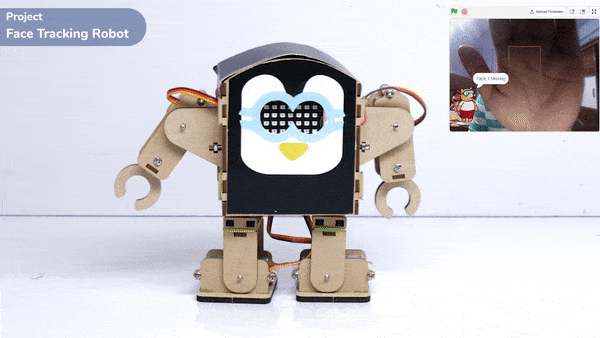
Code omnidirectional robot!
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
-
 Object Declaration in Python: meca = Mecanum(1, 2, 7, 8)
Object Declaration in Python: meca = Mecanum(1, 2, 7, 8)
-
 Extension Catergory: Quarky
Extension Catergory: Quarky
Introduction
PictoBlox Blocks
Scripts that wear this block will activate once the Green Flag has been clicked — these scripts can activate other scripts and enable the entire program. Without this block, the only way a project could run would be that it would sense the pressing of a key or clicking a sprite; the project would only last until all scripts depending on the starting scripts have ended.
The block checks if the first value is less than the second value. If it is less, the block returns true; if not, it returns false. This block works with letters too, as well as numbers. In Scratch, letters at the top of the alphabet (e.g. a, b, c) are worth less than letters at the end (e.g. x, y, z).
The speak () block uses the text-to-speech tool to speak the given text. It will speak the selected voice with the chosen language in the set language to () block. Usage of the block is limited to 128 characters. If a string longer than 128 characters is given, then only the first 128 characters will be spoken.
The block will play the specified instrument for the specified amount of seconds using a sampled percussion instrument. Even though the block uses the word “drum”, the choices in the drop-down menu are many different percussion instruments including drums, triangles, bongos, cowbell, vibraslap, and various idiophones.
When used in a script, the sprite will produce a bitmap image of itself which is stamped onto the stage. (Because it is merely a picture of the sprite and not a sprite itself, it cannot be programmed.) Like other Pen blocks, the Stamp block will not draw over sprites. The erase all block removes all stamped images.
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Block Coding Examples
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Python Functions
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the current backdrop, for the handwritten and printed text.
Syntax: analysebackdrop()
The function sets the current servo motors to the specified angle for the pick and place robot.
Syntax: setarmangle(angle = 90)
The function returns a tuple. The first element is a boolean and the second is the frame of the video.
Syntax: cap.read()
The function performs the selected action for the quadruped. The action runs for the specified times and at the specified speed.
Syntax: action(action = “dance1”, time period = 1000, cycle = 1)
The function reports the state of the IR sensor connected to the selected pin. The function returns 1 when it is HIGH (or 3.3V) or 0 when it is LOW (or 0V).
Syntax: irstatus(pin = “D3”)
The function deletes the feed with the specified name in the Adafruit IO account.
Syntax: adaio.deletefeed(feedname = “feed name”)
The function makes the servo motors connected to the wheels orient towards the left. This orientation is used for making the robot turn left in a circle.
Syntax: setleftturnangle(Angle = 40)
The function performs the selected motion for the humanoid. The motion runs for the specified times and at the specified speed.
Syntax: move(motion = “forward”, time period = 1000, cycle = 1)
The function allows the robot to cease all activity by stopping all its motors.
Syntax: stoprobot()
The function sets the analog state of the specified pin to the specified value between 0 to 255.
Syntax: setanalogoutput(servo port = 1, PWM = 50)
The function is a unary operation that calculates the inverse hyperbolic sine of a given value.
Syntax: math.asinh(x)
This function moves the end-effector of a robotic arm to a desired point in 3-dimensional space. The X, Y, and Z coordinates must be specified, as well as a parameter to set the time of movement. The function takes these inputs and sends commands to the robotic arm to move to the specified location in the desired time period.
Syntax: roboticArm.movetoxyz(XPOS = 0, YPOS = 150, ZPOS = 70, TIME = 1000)
This function sets the motor speed for the robot’s turns.
Syntax: setturingspeed(turn_speed = 50)
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the camera, for faces.
Syntax: analysecamera()
The function sets its sprite’s X and Y position to that of the mouse-pointer or another sprite — in other words, it moves the sprite to a random position, the mouse-pointer, or another sprite.
Syntax: goto(moveto = “_random_”)
The function changes the Stage’s backdrop to the specified one.
Syntax: switchbackdrop(backdrop_name = “backdrop1”)
The function changes the specified sound effect to the value. The input is for selecting how much the sound will be changed. A positive number will make the sound effect have more effect, while a negative number will make it smaller.
Syntax: setsoundeffect(effect_name = “PITCH”, effect_value = 100)
The function returns the most recent text imputed with the input() function. When nothing has been inputted yet, the value will hold nothing.
Syntax: answer()
The function checks if the specified key is pressed. If the key is being pressed, the block returns “true”; if it is not, it returns “false”.
Syntax: iskeypressed(key = “space”)
The function sets the pen’s color to the given color – (R, G, B).
Syntax: setcolor(color = [0, 0 , 0])
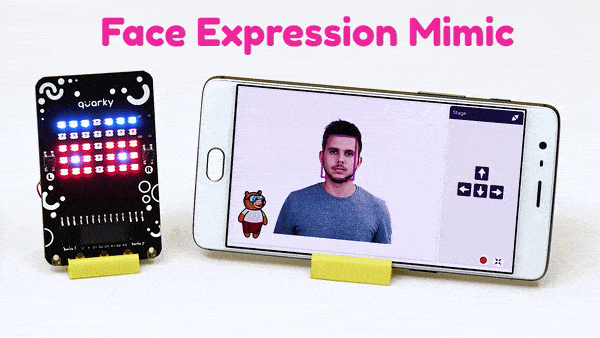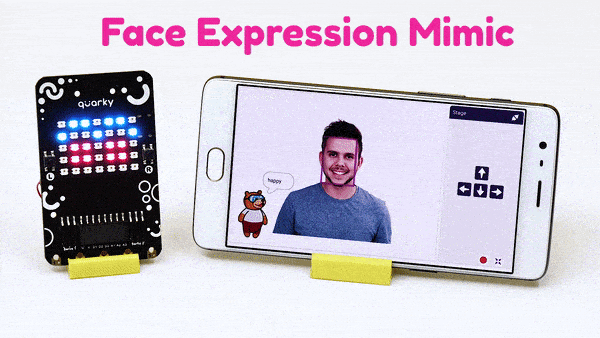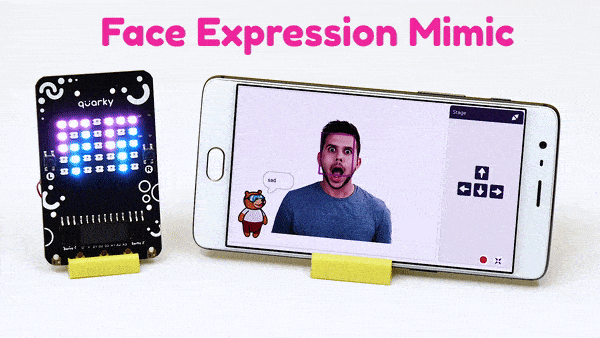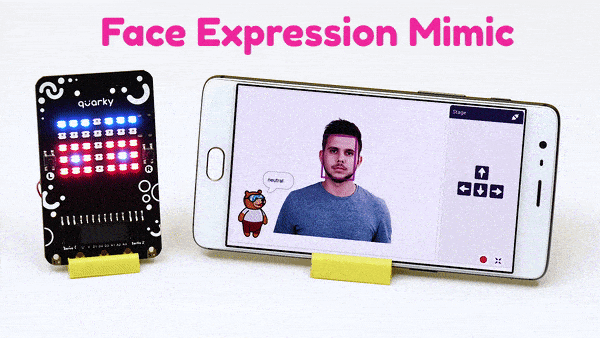
The function sets the RGB LED display matrix to the emotion specified: “happy”, “angry”, “crying”, “super angry “, “surprise”, “basic”, “love”, “nerd”, “reject”, “wave”, “thinking”, “giggle”, and “disco”.
Syntax: showemotion(pattern = “happy”)
The function returns the state of the specified touch sensor of Quarky. If the touchpad is touched it will return True, else False.
Syntax: ispadtouched(touch_pin = 1)
The function performs the automatic line following logic with the parameters specified in the initializelinefollower() function.
Syntax: dolinefollowing()
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the current costume, for the feature.
Syntax: analysecostume()
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the current costume of the sprite, for the handwritten and printed text.
Syntax: analysecostume()
The function moves the servo motors of the pick and place robot to the pick angle specified by the user.
Syntax: pick()
The function flips a 2D array around vertical, horizontal, or both axes.
Syntax: cv2.flip(input_array, flip_code = 1)
Resizing an image means changing its dimensions of it, be it width alone, height alone, or changing both of them. Also, the aspect ratio of the original image could be preserved in the resized image. To resize an image, OpenCV provides cv2.resize() function.
Syntax: cv2.resize(image_array, dsize = (224,224))
The function sets the servo motors of the quadruped to the specified angles at the specified speed.
Syntax: moveall(servo angles = [90,90,90,90,90,90,90,90], time = 1000)
The function reports the temperature or humidity from the DHT sensor connected to the selected pin.
Syntax: dhtmeasure(parameter = “temperature”, pin = “D3”)
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Python Coding Examples
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Table of Contents