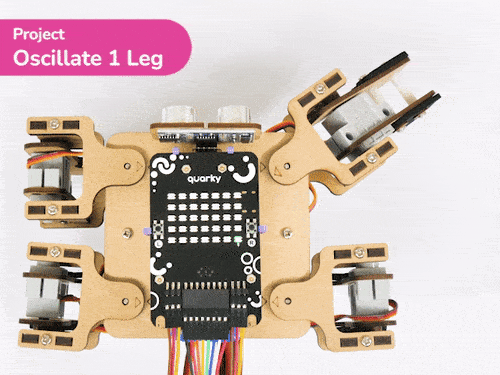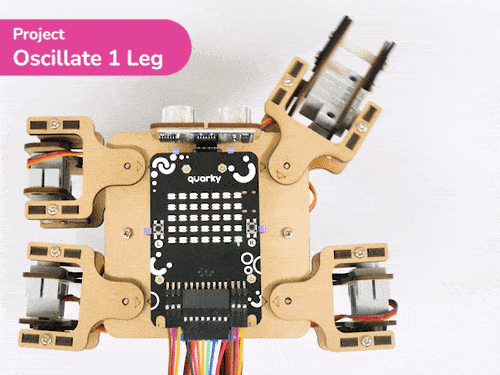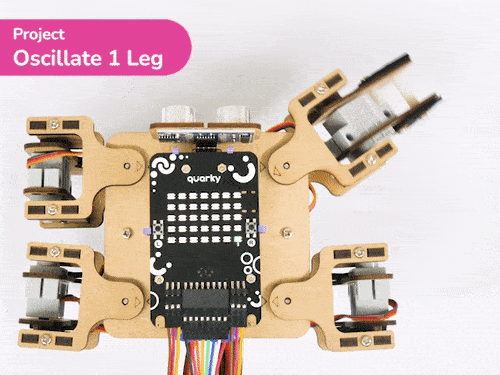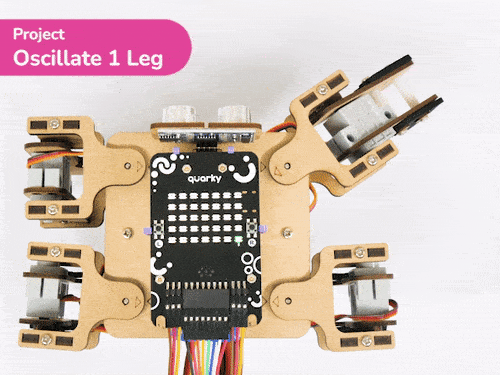
[PictoBloxExtension]
Quarky Advance Line Following
Extension Description
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
-
 Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
-
 Extension Catergory: Quarky
Extension Catergory: Quarky
Introduction
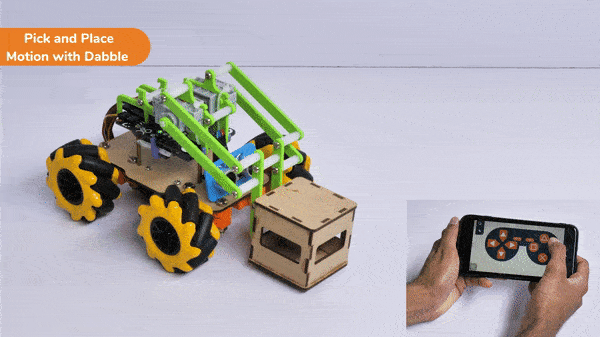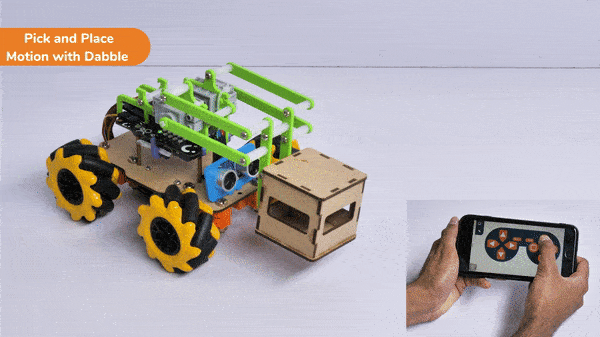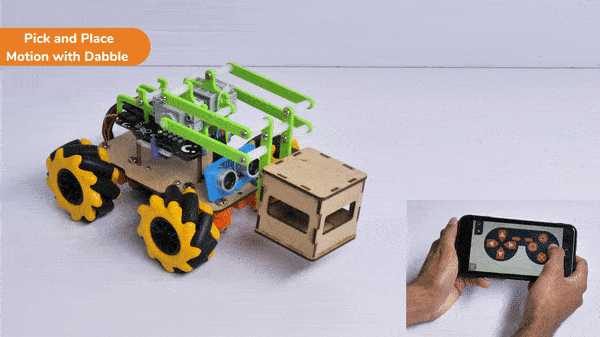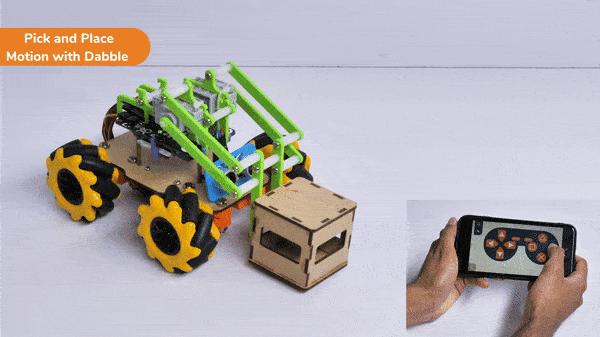
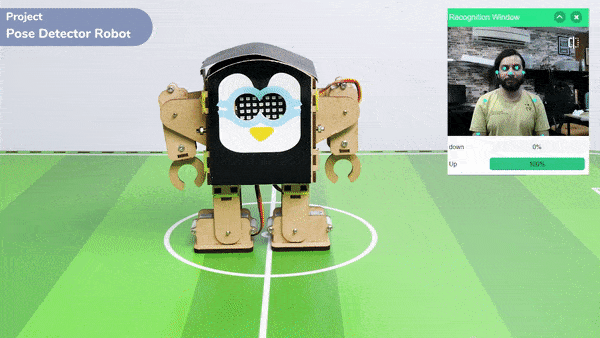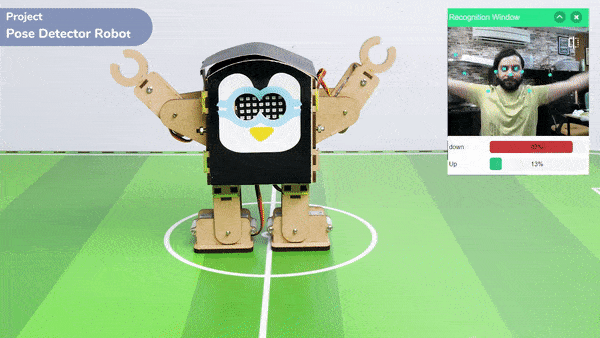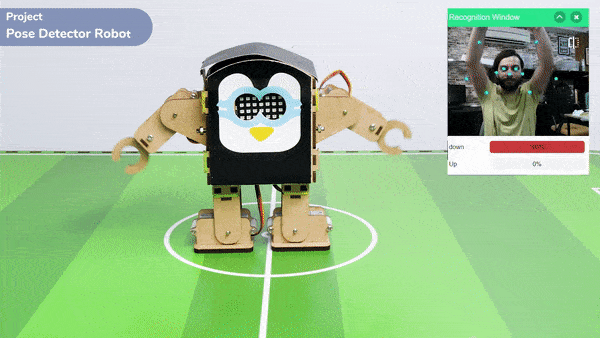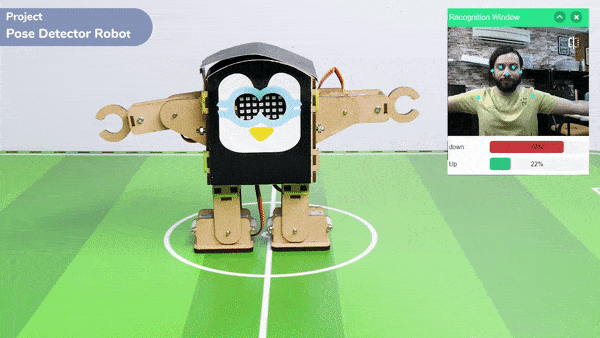
The extension helps you to speed up your quarky in the line following using blocks and Python functions.
Read More
PictoBlox Blocks
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Block Coding Examples
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Python Functions
If the sprite is showing, it will hide the sprite. If the sprite is already hidden, nothing happens.
Syntax: hide()
The function set the steering orientation to the left for the Steering Robot.
Syntax: left()
The block resets the timer running for the oscillator to 0.
Syntax: resetoscillationtimer()
The function reports the moisture reading from the sensor. The value varies from 0 to 100%.
Syntax: readmoisture()
The function sends the data to the ThingSpeak channel. The data is added to field 1 of the channel.
Syntax: ts.senddatatocloud(data = 100)
The function executes the oscillator according to stored parameters for the servo motor and the current time.
Syntax: executeoscillator()
The function sets the port of the servo motor for the gripper robot in the code, making it easier to control.
Syntax: initialisegripper(servo port = 4)
This function takes two parameters – a value for the angle at which the gripper should open and a value for the angle at which the gripper should close – and sets the angles for the gripper on a robotic arm.
Syntax: roboticArm.setgripperangle(OPEN = 0, CLOSE = 50)
The function returns the x position of the specified landmark point of the specified face with respect to the stage.
Syntax: landmarksx(face = 1, landmark = 1)
The function moves its sprite’s Y position by the specified amount.
Syntax: changey(delta_y = 10)
The function will place a sprite in front of all other sprites. It does this by changing the sprite’s layer value.
Syntax: gotolayer(postition = “front”, layer_number = 1)
The function set the steering orientation to the right for the Steering Robot.
Syntax: right()
The function reports the time passed from the reset for the oscillator.
Syntax: oscillationtimer()
The function initializes the RFID sensor. The function is important to run at the start to use other functions of the RFID sensors.
Syntax: initialiserfid()
The function sends multiple data to the ThingSpeak channel. The data is mapped to the 8 fields of the ThingSpeak channel.
Syntax: ts.sendmultipledatatocloud(field_data_1 = 100, field_data_2 = 100, field_data_3 = 100, field_data_4 = 100, field_data_5 = 100, field_data_6 = 100, field_data_7 = 100, field_data_8 = 100)
The function executes the oscillator according to stored parameters for the servo motor and the current angle specified in the functions.
Syntax: executesscillatorat(angle = 90)
The function executes the oscillator for the specified cycles.
Syntax: oscillateforcycles(cycles = 1)
The function sets the angle of a robot’s gripper servo motor to a specified value.
Syntax: setgripperangle(angle = 90)
This function used to control the opening and closing of the robotic arm gripper.
Syntax: roboticArm.gripperaction(STATE = “open”)
The function returns the y position of the specified landmark point of the specified face with respect to the stage.
Syntax: landmarksy(face = 1, landmark = 1)
The function sets its sprite’s Y (up and down) position to the specified amount.
Syntax: sety(y = 27)
The function changes its sprite’s layer value by the specified amount. This function is rather unusual compared to other functions. It moves the layer value back, and not forward. To move it forward instead, a negative number can be used.
Syntax: changelayer(postition = “forward”, layer_number = 1)
The function set the steering orientation to straight for the Steering Robot.
Syntax: straight()
The function activates the RFID sensor to read any nearby RFID tags for the specified time. Once identified, the value of the reading is stored in the local system which can be used from the other functions. The function also reports whether the operation is completed or not. If any RFID tag is scanned the block returns 1, else it returns 0.
Syntax: readrfid(duration = 5)
The function gets the data from the ThingSpeak channel and stores the 8 field values in PictoBlox or Quarky.
Syntax: ts.getdatafromthingspeak()
The function resets the timer running for the oscillator to 0.
Syntax: resetoscillationtimer()
This function sets the angle of the Gripper Robot’s gripper servo motor to a particular value when it is in the closed position.
Syntax: setcloseangle(angle = 40)
This function takes the servo motor as the input parameter, and it returns the corresponding angle of the servo as an output.
Syntax: roboticArm.getcurrentservoangle(SERVO = “link1”)
The function allows the user to add a particular face into the database from the camera feed. The user can specify the name of the face with the argument as well. This addition of the face in the database is also stored inside the PictoBlox file while saving.
Syntax: addclassfromcamera(label_number = 1, label_name = “Jarvis”)
The function checks to see if its sprite is touching the edge of the screen with the move steps block — and if it is, the sprite will point in a direction that mirrors the direction from which it is coming. It uses a line perpendicular to the edge to determine the reflection angle.
Syntax: bounceonedge()
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Table of Contents