[PictoBloxExtension]
Quarky Advance Line Following
Extension Description
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
-
 Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
-
 Extension Catergory: Quarky
Extension Catergory: Quarky
Introduction
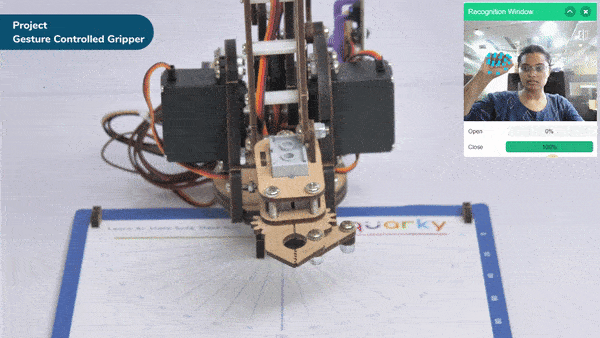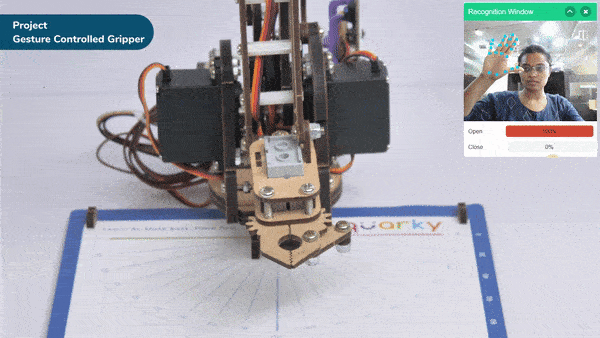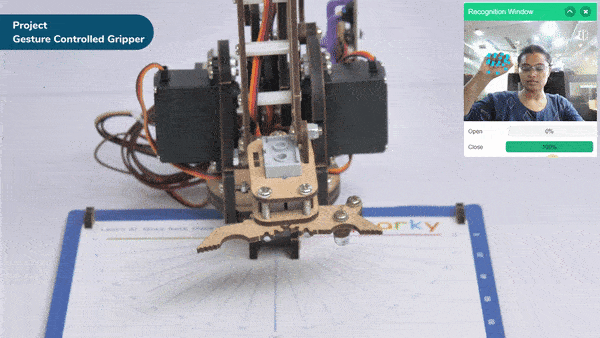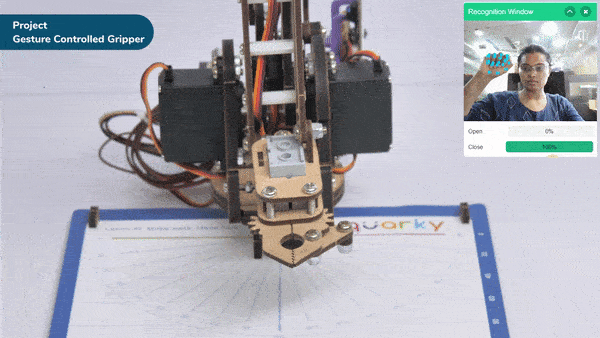
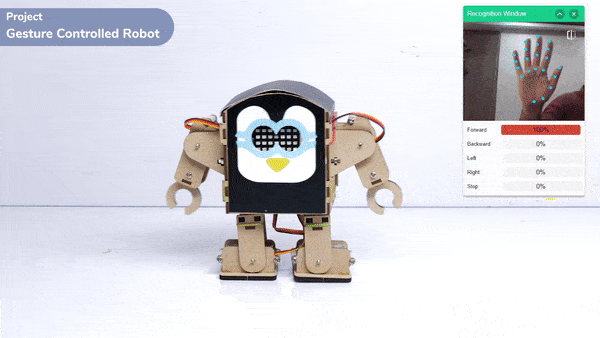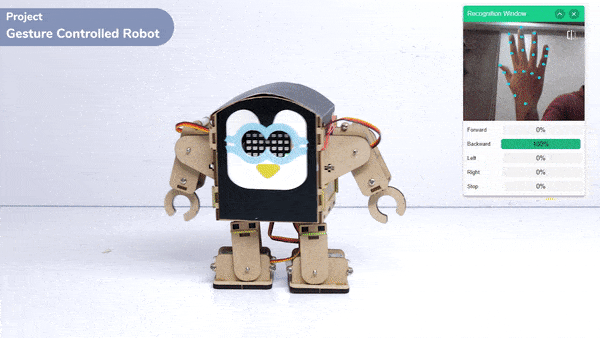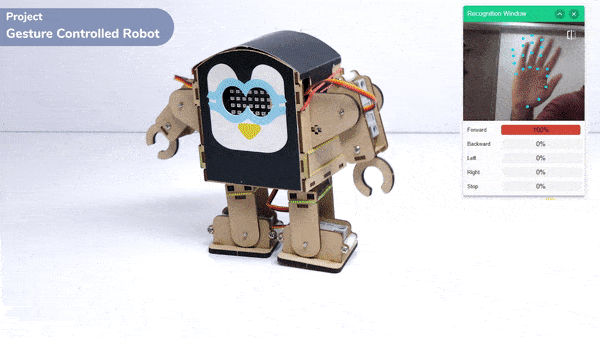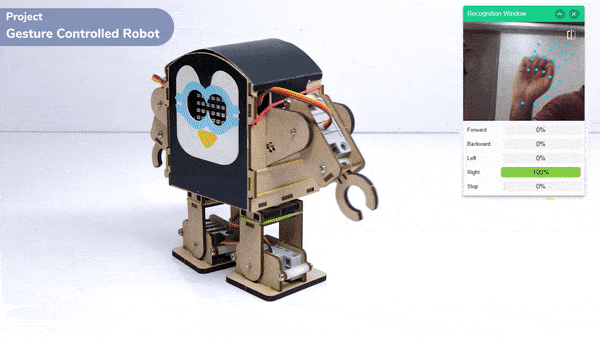
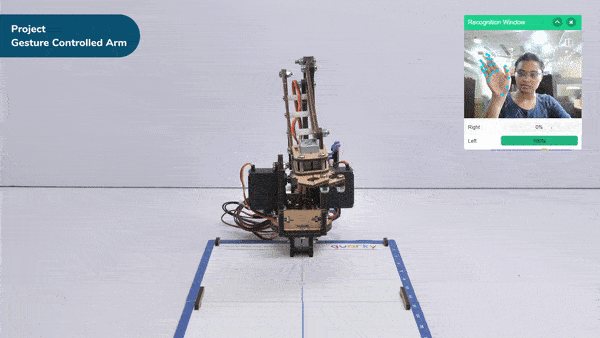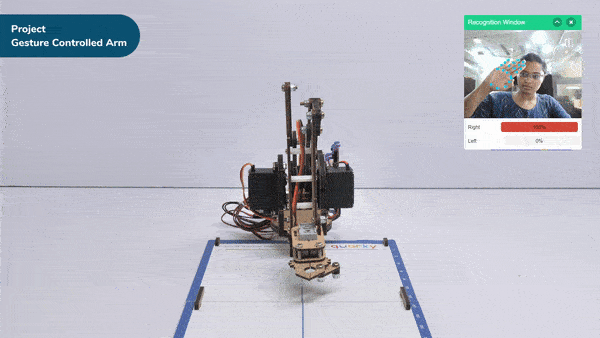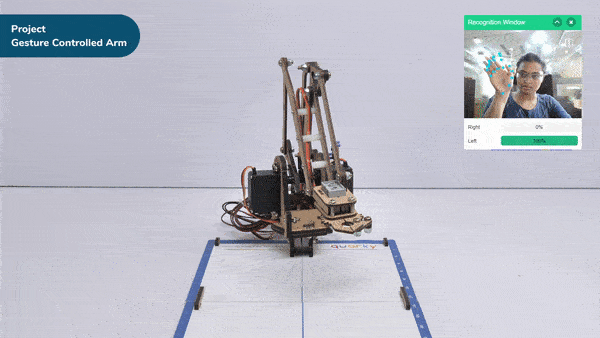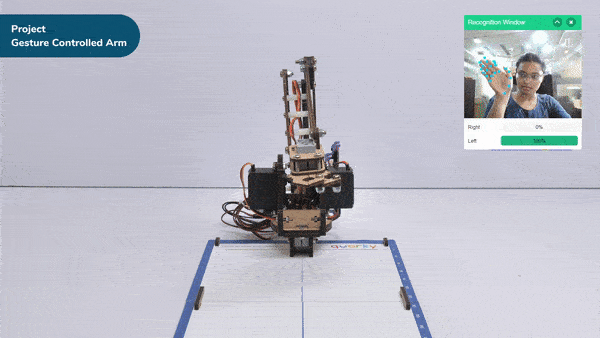
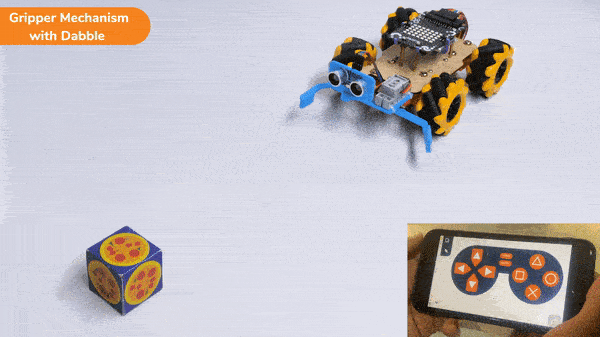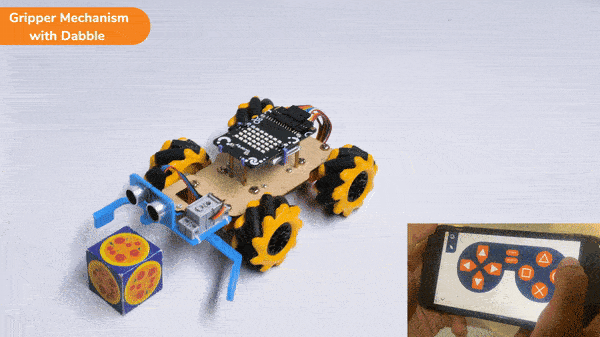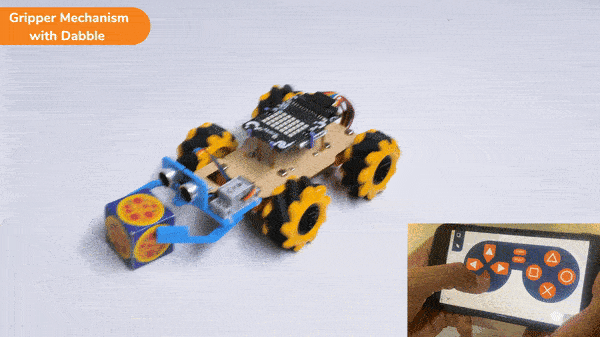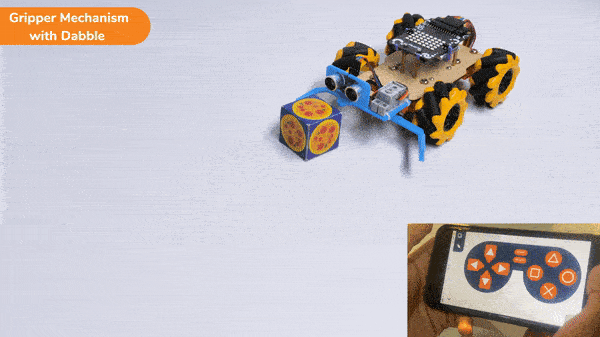
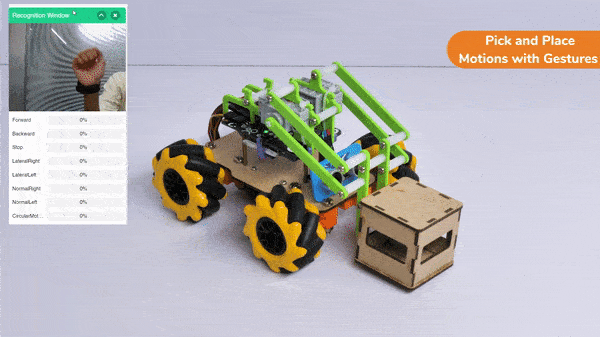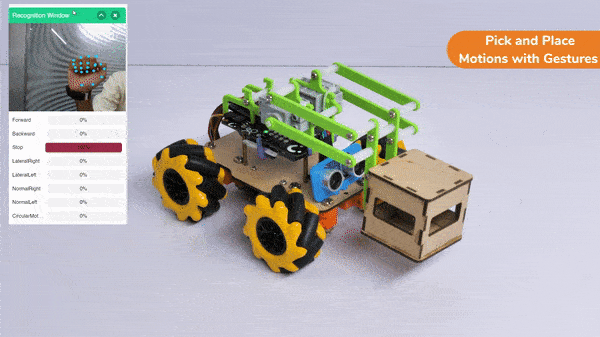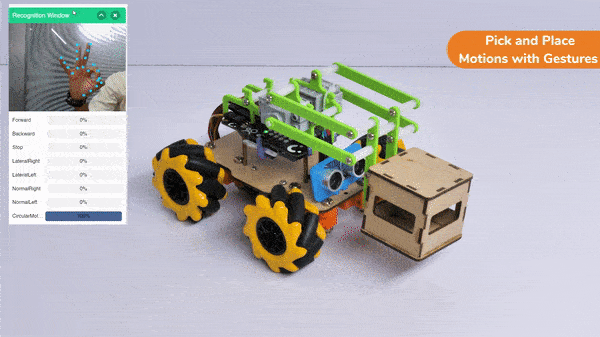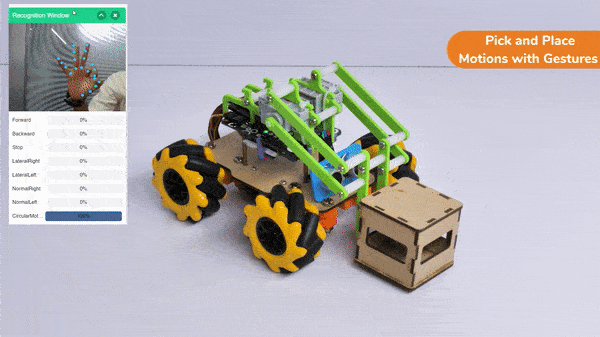
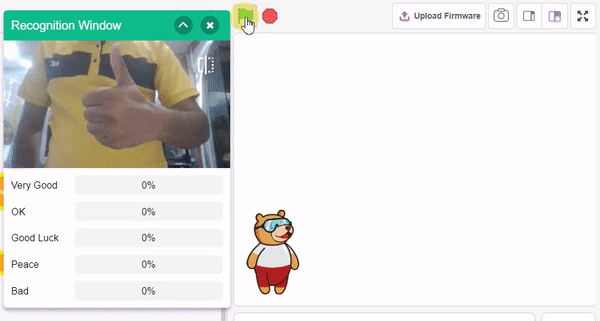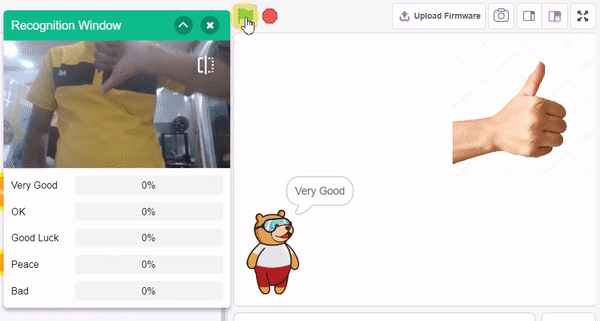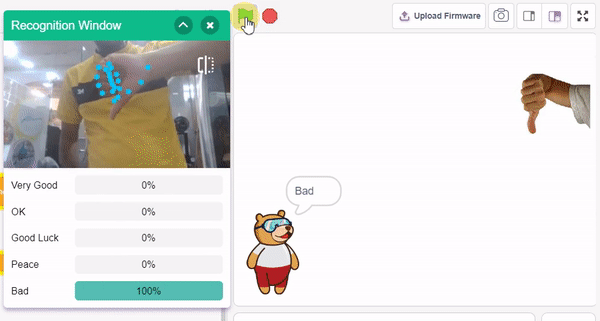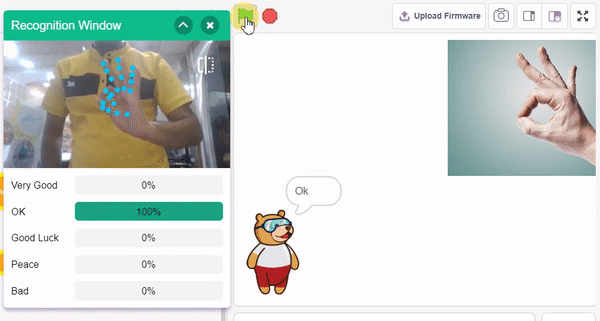
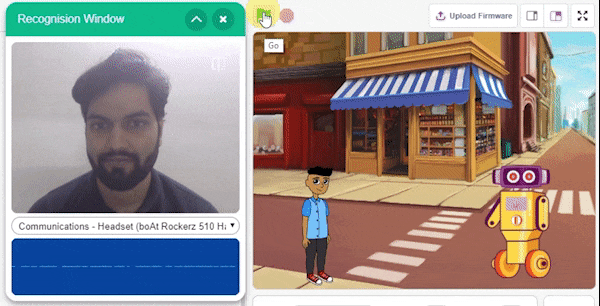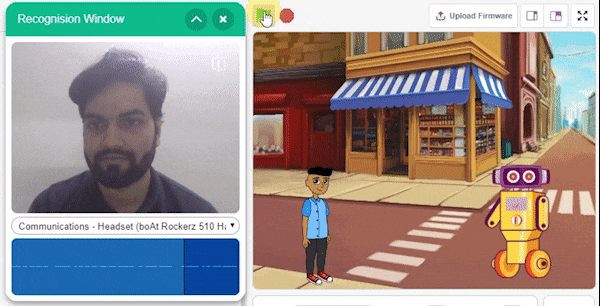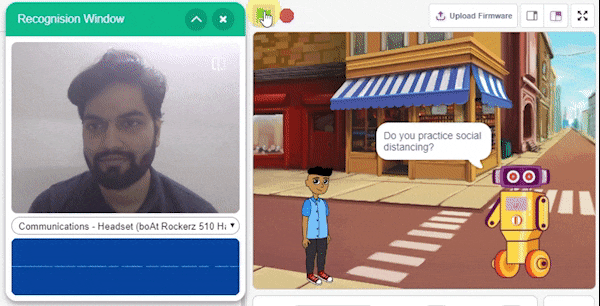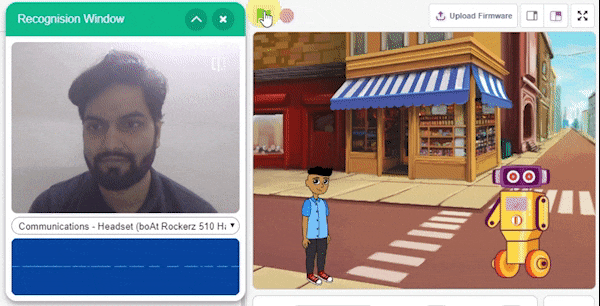
The extension helps you to speed up your quarky in the line following using blocks and Python functions.
Read More
PictoBlox Blocks
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Block Coding Examples
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Python Functions
The function changes its sprite’s size by the specified amount. The default sprite size is 100; size values below that percentage are for shrunken sprites, and size values above it are for overlarge sprites.
Syntax: changesize(percentage = 10)
The function changes the volume of a sprite by the specified amount.
Syntax: changevolume(volume = -10)
The function reports the mouse pointer’s current y position on the stage.
Syntax: mousey()
The function sets the Pen Size to the given number. The pen draws a trail of circles. The diameter of the circle, in pixels, is equal to the pen size.
Syntax: setsize(size = 1)
The function sets the RGB LED display matrix to display the specified pattern: “rainbow”, “rainbow strip”, “cloud colors”, “party colors”, “forest colors”, and “lava colors”.
Syntax: showpattern(pattern = “rainbow”)
The function returns the distance reading from the specified ultrasonic sensor.
Syntax: getdistance(sensor_number = 1)
The function sets the specified motor of the Quarky robot to the specified direction (“FORWARD” or “BACKWARD”) and specified speed.
Syntax: runmotor(motor = “L”, direction = “FORWARD”, speed = 100)
The function reports the number of specified features to count in the image. The options are celebrities, brands, objects, and image tags in a single image can be reported.
Syntax: imagefeaturecount(feature_type = “object”)
The function reports the handwritten text identified from the analysis.
Syntax: handwrittentextresult()
The function sets the Quarky Gripper Robot’s gripper servo motor angle for a close position to the specified value.
Syntax: setcloseangle(angle = 90)
Keras models can be used to detect trends and make predictions, using the model.predict() function.
Syntax: model.predict(image_array)
The function reports the analog reading of the LDR (Light) sensor connected to the selected pin. The value will vary between 0 to 4095.
Syntax: ldrvalue(pin = “A1”)
The function gets the last color value from the specified feed and stores it in PictoBlox or Quarky.
Syntax: adaio.getcolordata(feedname = “feed name”)
The function sets the servo motors of the head to the specified angle.
Syntax: setheadangle(Angle = 90)
The function sets the servo motors of the humanoid hand to the specified angles at the specified speed.
Syntax: movehand(time = 1000, servo angles = [90,90])
The function sets the ports for the left and right servo motors of a pick-and-place robot.
Syntax: initialisepickplace(left servo = 5, right servo = 4)
The function reverses the forward direction of the specified motor of the Quarky Expansion Board.
Syntax: reversemotordirection(motor port = 1)
The function is used to calculate the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a given value.
Syntax: math.atanh(x)
This function creates a clockwise circle trajectory in the Y plane for a robotic arm, given the center position in the X and Z axes, and the radius of the circle. The function calculates the points on the trajectory and sends instructions to the arm to travel to each point sequentially.
Syntax: roboticArm.moveincircleclockwise(XPOS = 0, ZPOS = 80, RADIUS = 50, YPOS = 180, TIME = 4000)
This function sets the three pins for IR sensors used in line following for left, middle, and right detection.
Syntax: setirsensor(set_left = ‘D1’, set_middle = ‘D2’, set_right = ‘D3’)
This function is used to get the expression of the analyzed face. The parameter can be used to select the identifying number of the face whose expression is to be analyzed.
Syntax: expression(face = 1)
The function sets its sprite’s size to the specified amount. The default sprite size is 100%; anything lower than that will decrease the size of the sprite on the stage, and anything above will increase the size of the sprite on the stage.
Syntax: setsize(percentage = 100)
The function sets its sprite’s volume to the specified amount. It only affects the sprite (or the Stage) that the block is in.
Syntax: setvolumeto(volume = 100)
The function changes the pen size by the specified amount.
Syntax: changesize(size = 1)
The function sets the brightness of the RGB LED display matrix.
Syntax: setbrightness(brightness = 20)
The function returns the state of the digital sensor connected to the specified pin of the Quarky.
Syntax: readdigitalsensor(digital_pin = “D1”)
The function stops the specified motor of the Quarky.
Syntax: stopmotor(motor = “L”)
The function reports the name/x position/y position/width/height or confidence of the recognized celebrity/brand/object/image tag. If the number is out of range, then the function will return NULL.
Syntax: imagefeatureinfo(feature_type = “object”, number = 1, information = “name”)
The function reports the printed text identified from the analysis.
Syntax: printedtextresult()
The function sets the Quarky Gripper Robot’s gripper servo motor angle for an open position to the specified value.
Syntax: setopenangle(angle = 90)
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Table of Contents