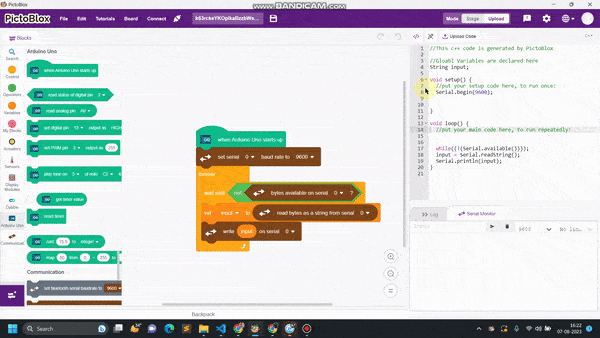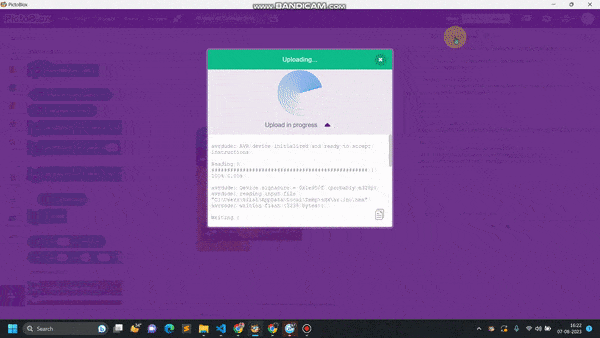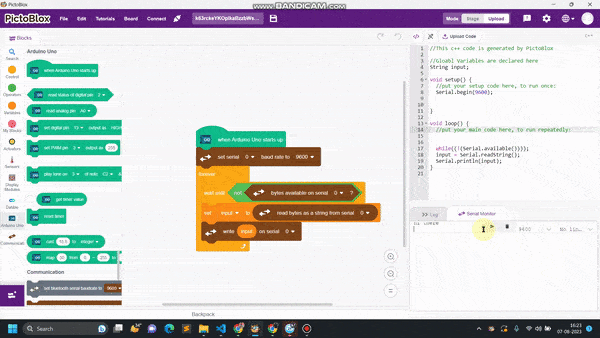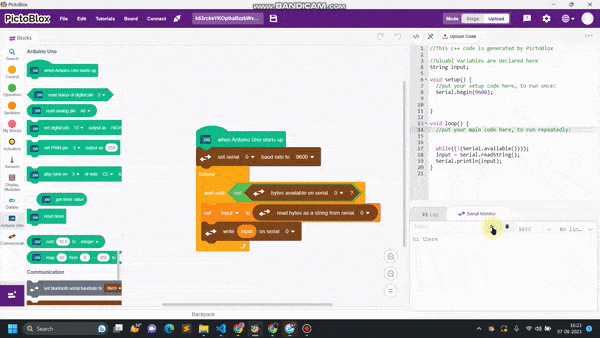
[PictoBloxExtension]
Quarky Advance Line Following
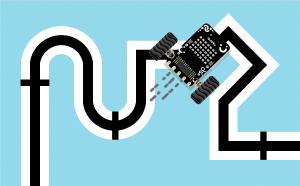
Extension Description
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
-
 Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
-
 Extension Catergory: Quarky
Extension Catergory: Quarky
Introduction
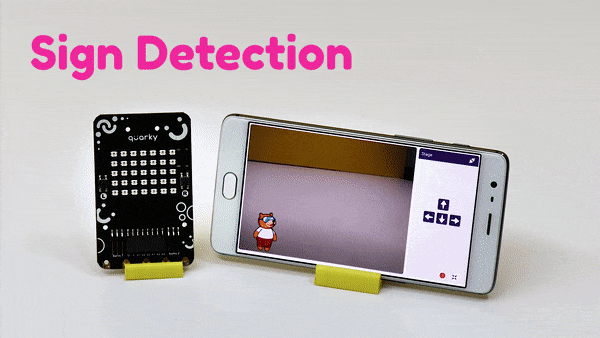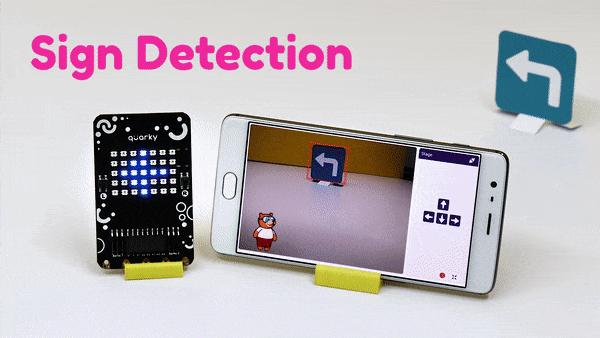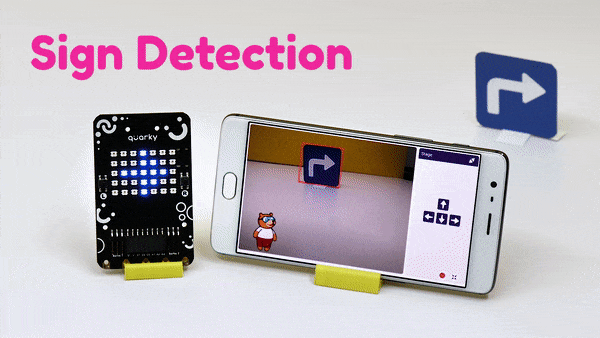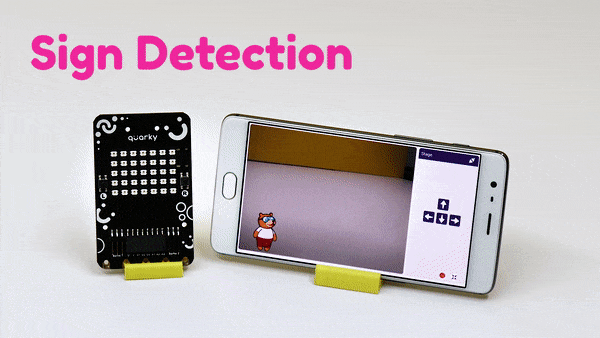
The extension helps you to speed up your quarky in the line following using blocks and Python functions.
Read More
PictoBlox Blocks
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Block Coding Examples
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Python Functions
The function enables the automatic display of the landmark on pose/hand detected on the stage.
Syntax: enablebox()
The function disables the automatic display of the landmark on pose/hand detected on the stage.
Syntax: disablebox()
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the stage, for human pose detection.
Syntax: analysestage()
This function returns the x position of the pose landmark detected. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: x(landmark_number = 1, pose_number = 1)
This function returns the y position of the pose landmark detected. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: y(landmark_number = 1, pose_number = 1)
The function tells whether the human pose is detected or not.
Syntax: isdetected(landmark_number = 1, pose_number = 1)
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the camera, for human hand detection.
Syntax: analysehand()
The function tells whether the human hand is detected or not.
Syntax: ishanddetected()
This function returns the specified parameter of the hand landmark detected.
Syntax: gethandposition(parameter = 1, landmark_number = 4)
This function returns the x position of the hand detected. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: handx()
This function returns the y position of the hand detected. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: handy()
The function adds the specified text data to the specified class.
Syntax: pushdata(text_data = “your text”, class_label = “class”)
The function trains the NLP model with the data added with pushdata() function.
Syntax: train()
The function resets and clears the NLP model.
Syntax: reset()
The function analyses the specified test and provides the class name under which it has been classified by the NLP model.
Syntax: analyse(text = “your text”)
The function is used to control the state of the camera.
Syntax: video(video_state = “on”, transparency = 1)
The function enables the automatic display of the box on object detection on the stage.
Syntax: enablebox()
The function disables the automatic display of the box on object detection on the stage.
Syntax: disablebox()
This function is used to set the threshold for the confidence (accuracy) of object detection, 0 being low confidence and 1 being high confidence.
Syntax: setthreshold(threshold = 0.5)
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the camera, for objects.
Syntax: analysecamera()
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the stage, for objects.
Syntax: analysestage()
This function returns the total number of objects detected in the camera feed or the stage.
Syntax: count()
This function is used to get the class name of the analyzed object.
Syntax: classname(object = 1)
This function returns the x position of the object detected. You can specify the object for which the value is needed. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: x(object = 1)
This function returns the y position of the object detected. You can specify the object for which the value is needed. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: y(object = 1)
This function returns the width of the object detected. You can specify the object for which the value is needed. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: width(object = 1)
This function returns the height of the object detected. You can specify the object for which the value is needed. The position is mapped with the stage coordinates.
Syntax: height(object = 1)
This function is used to get the confidence (accuracy) of object detection, 0 being low confidence and 1 being high confidence.
Syntax: confidence(object = 1)
The function returns whether the specified signal is detected in the analysis or not.
Syntax: issignaldetected(signal_name = “Go”)
The function returns the specified parameter for the specified signal detected.
Syntax: getsignaldetail(signal_name = “Go”, parameter_value = 1)
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Table of Contents