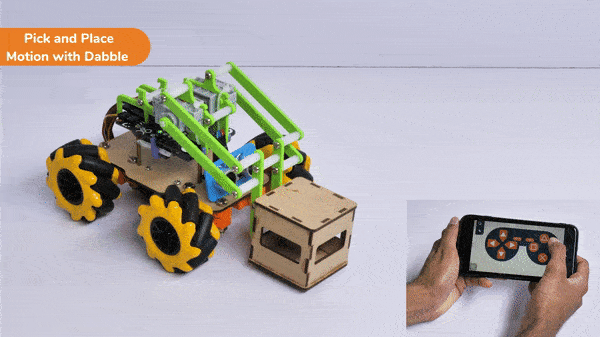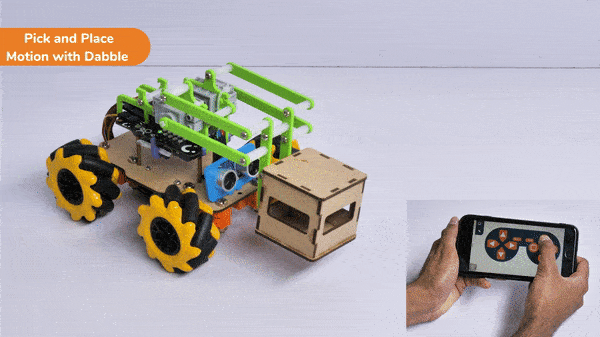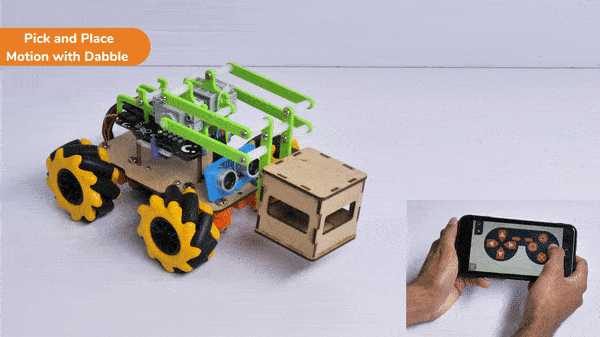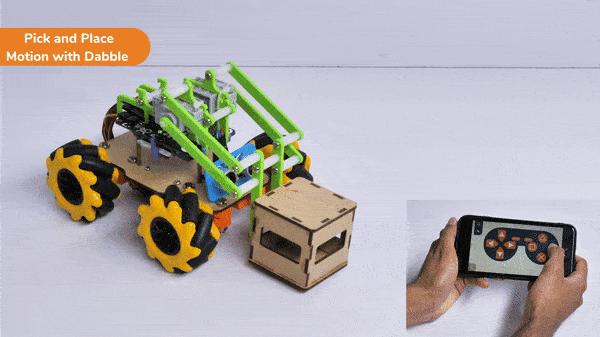
[PictoBloxExtension]
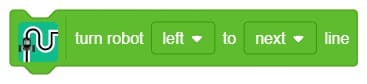
Quarky Advance Line Following
Extension Description
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
-
 Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
Object Declaration in Python: linefollow = quarkyAdvanceLineFollowing();
-
 Extension Catergory: Quarky
Extension Catergory: Quarky
Introduction
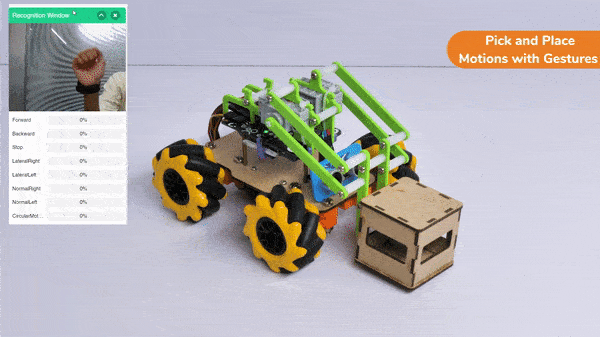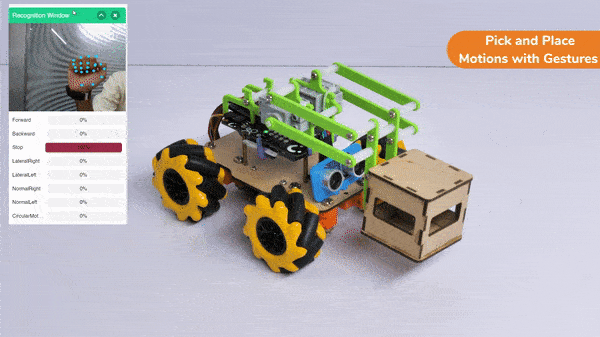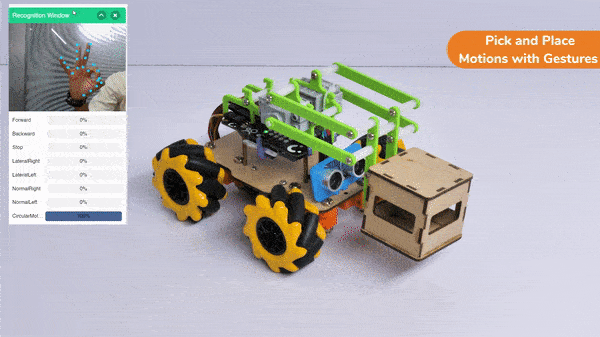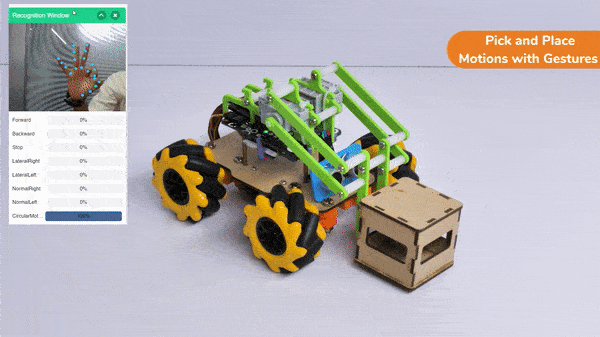
The extension helps you to speed up your quarky in the line following using blocks and Python functions.
Read More
PictoBlox Blocks
The block will check its Boolean condition. If the condition is true, the blocks held inside it will run, and then the script involved will continue. If the condition is false, the code inside the block will be ignored and the script will move on (unlike in the If () Then, Else block). The condition is only checked once; if the condition turns to false while the script inside the block is running, it will keep running until it has finished.
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Block Coding Examples
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Python Functions
The function returns its sprite’s current costume number or name.
Syntax: costume(result_type = “number”)
The function reports the data stored from the last RFID scan.
Syntax: readscanneddata()
The function reports the selected field data from the last read request from ThingSpeak.
Syntax: ts.getdatafromfield(field = 1)
The function reports the time passed from the reset for the oscillator.
Syntax: oscillationtimer()
This function sets the angle of the Gripper Robot’s gripper servo motor to a particular value when it is in the open position.
Syntax: setopenangle(angle = 90)
This function takes a single parameter as input and returns the current position of the end effector along a specified axis.
Syntax: roboticArm.getcurrentposition(AXIS = “x”)
The function allows the user to add a particular face to the database from the stage. The user can specify the name of the face with the argument as well. This addition of the face in the database is also stored inside the PictoBlox file while saving.
Syntax: addclassfromstage(label_number = 1, label_name = “Jarvis”)
The function changes the Rotation Style of the sprite in-project. Regardless of the style, the variable direction will still change.
Syntax: setrotationstyle(rotation_style = “left-right”)
The function writes the message to the RFID tag. It will wait for the specified time to scan an RFID tag and write the value on it. The function also reports whether the operation is completed or not. If the write is complete the block returns 1, else it returns 0.
Syntax: writetorfid(data = “Hello!”, duration = 5)
The block makes the specified type of HTTP request (GET, POST, or DELETE) on the specified URL. The request can have a body or not.
Syntax: makeapirequest(request = “GET”, url = “url”, bodytype = “with”)
This function allows the Gripper Robot to close its gripper.
Syntax: closearm()
The function deletes all the stored databases of the images for face recognition.
Syntax: deleteallclass()
The function returns the sprite’s X position.
Syntax: x()
The function returns the sprite’s Y position.
Syntax: y()
The function returns its sprite’s current backdrop number or name.
Syntax: backdrop(result_type = “number”)
The function sets the last scanned RFID tag to the master RFID tag. This can be used for authentication.
Syntax: setmaster()
The function defines the value of the body.
Syntax: setbody(body = “{“value”:”5″}”)
This function allows the Gripper Robot to open its gripper.
Syntax: openarm()
This function is used to match the input image from the camera with the stored classes previously stored in the database.
Syntax: recognisefromcamera()
The function returns the sprite’s direction in angle.
Syntax: direction()
The function returns its sprite’s size.
Syntax: size()
The function reports if the last RFID tag scanned is a master tag or not. If it is the master RFID tag, then it returns 1, else 0.
Syntax: ismaster()
The function sets the body content type to the specified value.
Syntax: setcontenttype(type = “application/x-www-form-urlencoded”)
This function is used to match the input image from the stage with the stored classes previously stored in the database.
Syntax: recognisefromstage()
The function reports the master RFID tag ID.
Syntax: getmastertag()
The function reports the request-response code received.
Syntax: requestapicode()
This function is used to check if the input image belongs to one of the classes previously defined. The class to be checked with can be set using the argument as label_number.
Syntax: isclassdetected(label_number = 1)
The function reports the last scanned RFID tag ID.
Syntax: gettag()
The function reports the body or error value from the HTTP request.
Syntax: getresponse(type = “body”)
This function is used to get the class of the input face detected from the analysis. The identifying number of the face being analyzed can be set using the argument.
Syntax: getclassname(face = 1)
All articles loaded
No more articles to load
Table of Contents