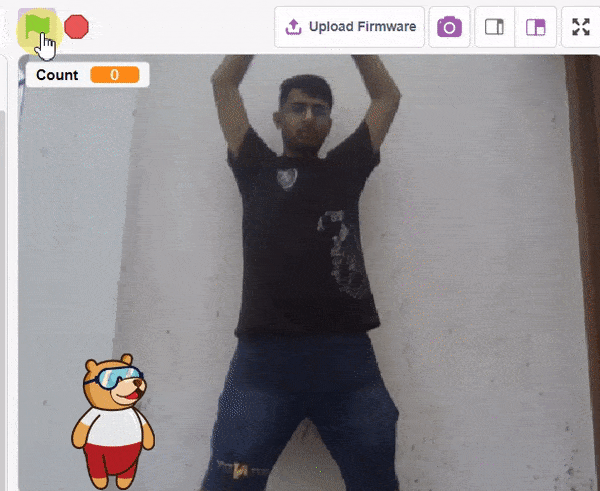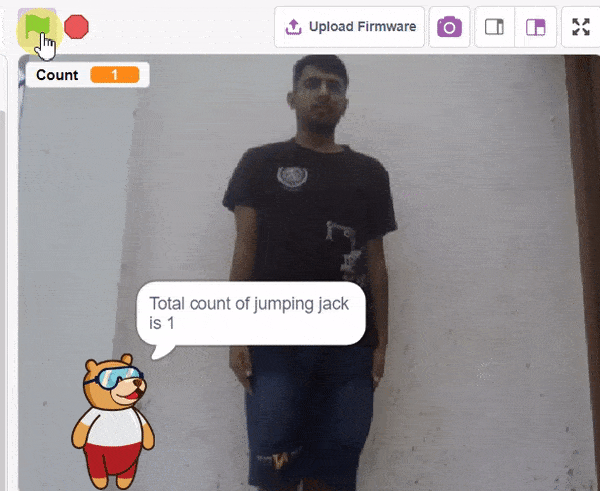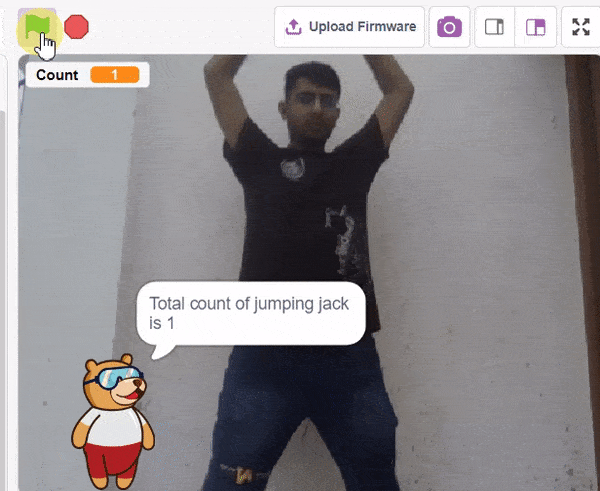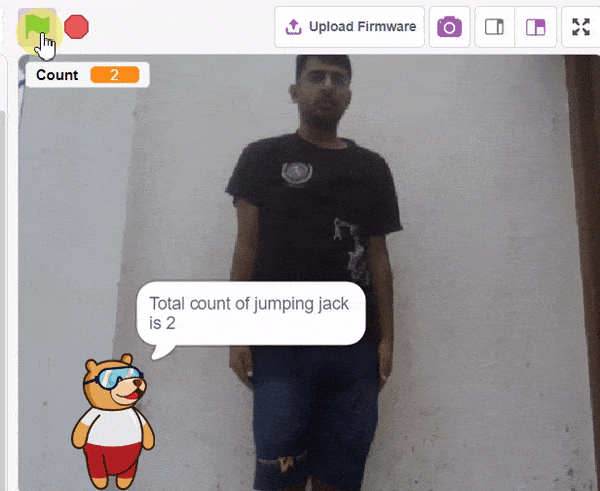
QR Code Scanner

-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode
Mode: Stage Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA, None
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA, None
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky, None
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky, None
-
 Object Declaration in Python: qr = QRCodeScanner()
Object Declaration in Python: qr = QRCodeScanner()
-
 Extension Catergory: Other
Extension Catergory: Other
Introduction
What is QR Code?
QR Code is a machine-scannable image that can be instantly read, using a smartphone camera. Every QR code consists of a number of black squares and dots that represent some encoded piece of information; like alphabets, numbers, etc. When your Smartphone scans this code, it translates that encoded information that only computers can understand, into something that can be easily understood by humans.

The QR Code Scanner extension allows users to scan QR codes from the camera or stage and report the information:
- QR Code Data
- QR code position on the stage
- QR code angle alignment on the stage
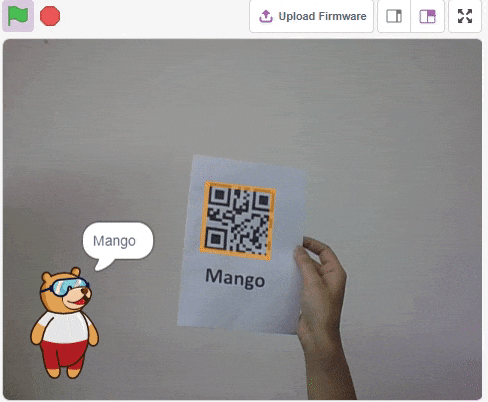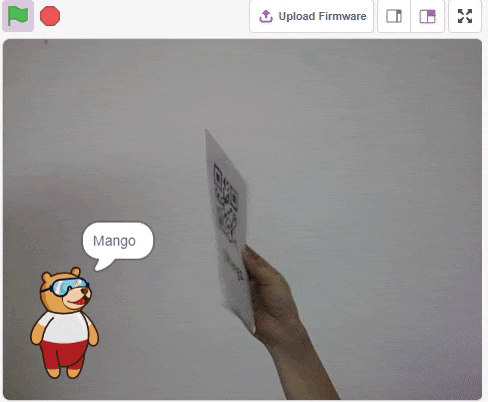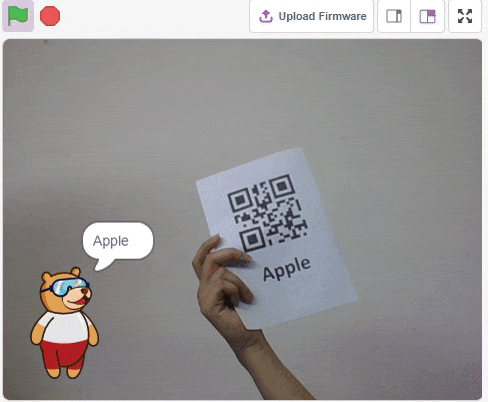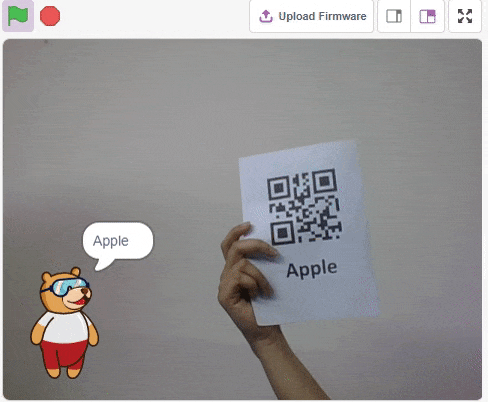
Accessing QR Code Scanner in Block Coding
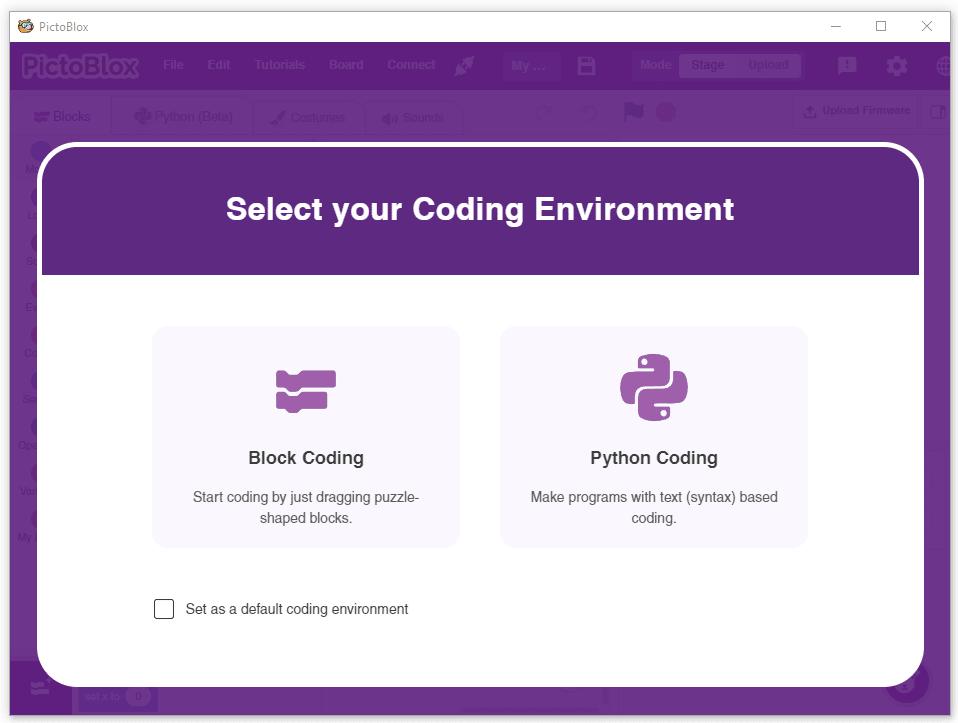
Following is the process to add QR Code Scanner capability to the PictoBlox Project.
- Open PictoBlox and create a new file.

- Select the coding environment as Block Coding.
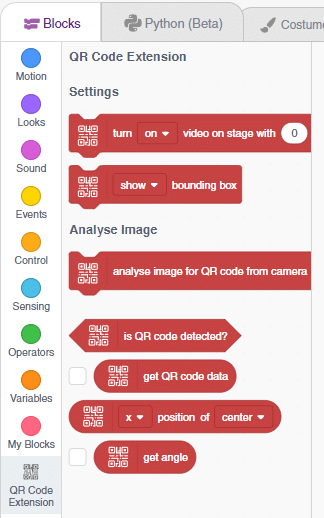
- Next, click on the Add Extension button and add the QR Code Scanner extension.

- You can find the QR Code Scanner blocks available in the project.
Accessing QR Code Scanner in Python Coding
Following is the process to add QR Code Scanner capability to the PictoBlox Project.
- Open PictoBlox and create a new file.
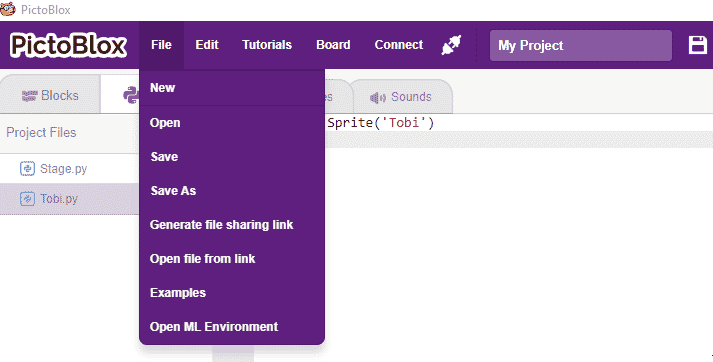
- Select the coding environment as Python Coding.

- Next, click on the Add Modules/Libraries button and add the QR Code Scanner extension.

- To access the library functions, you have to add the object declaration.
qr = QRCodeScanner()
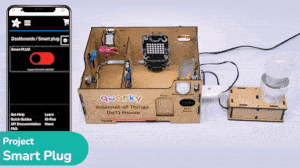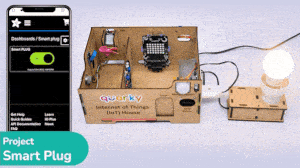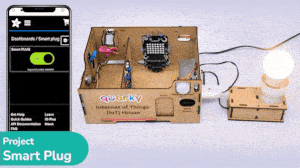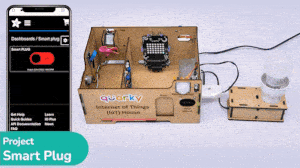
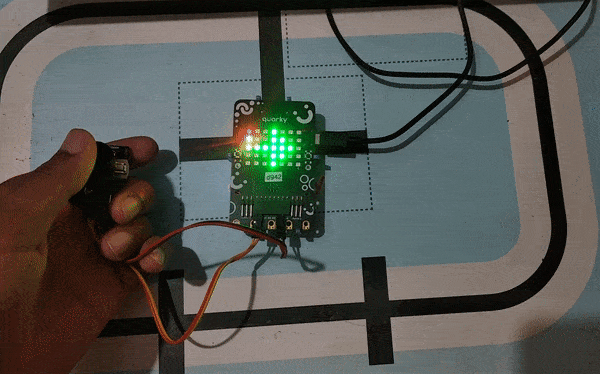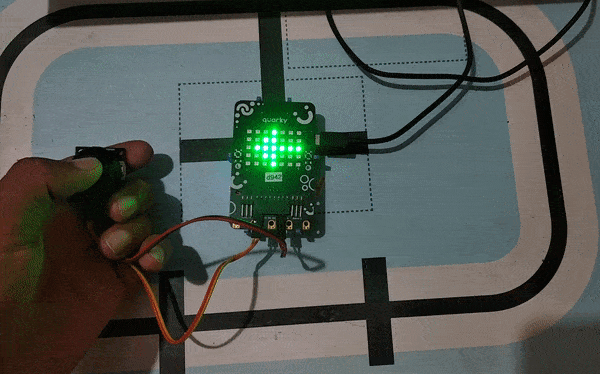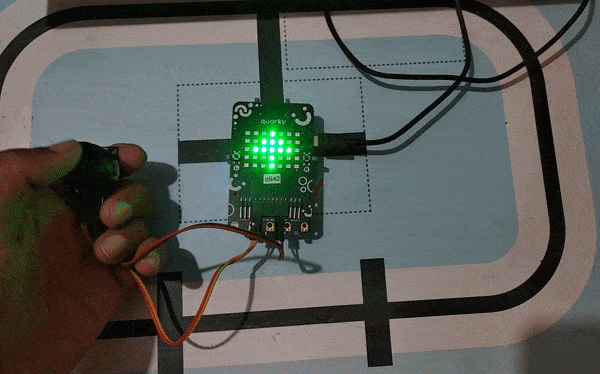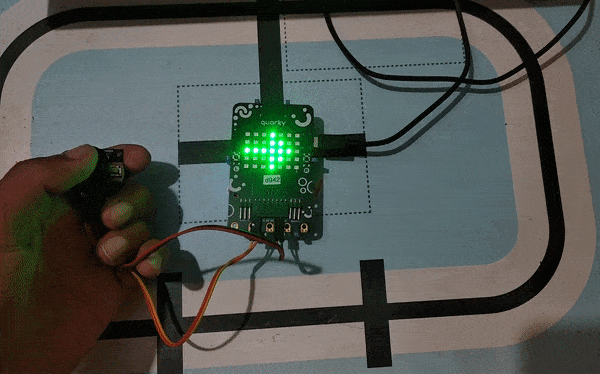
Example Project Video
In this project, a QR code is generated with the help of a QR code generator website. credits – https://www.qr-code-generator.com/
The QR code is linked to a URL. Then, the QR code is scanned with the help of the QR code scanner extension of Pictoblox. The project is created by RS Junction.