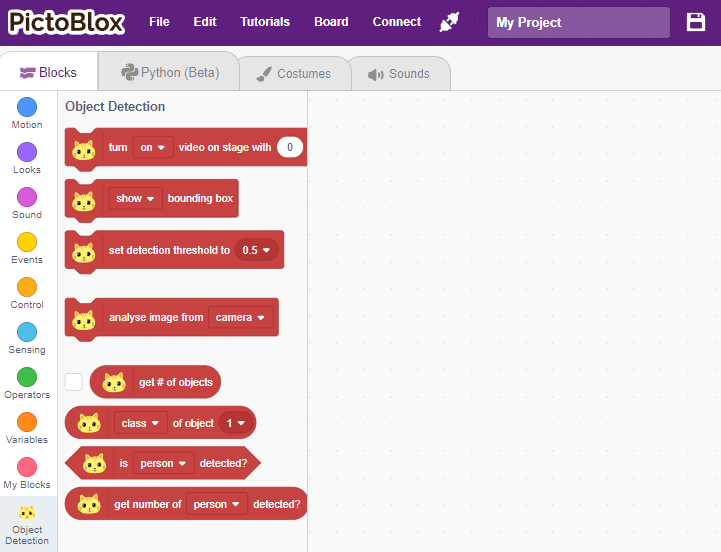
Object Detection
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode
Mode: Stage Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA, None
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA, None
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky, None
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky, None
-
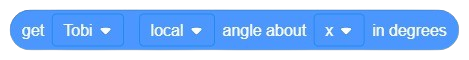
 Object Declaration in Python: od = ObjectDetection()
Object Declaration in Python: od = ObjectDetection()
-
 Extension Catergory: Artificial Intelligence
Extension Catergory: Artificial Intelligence
Introduction
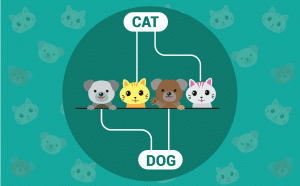
Object detection is used to locate and identify multiple objects in digital photographs. It is a computer vision technique that helps to detect objects as well as classify them. The object class may appear once or several times in the image. For example, in the following image, object detection assists us to locate the objects and classify them accordingly to the known set of objects.
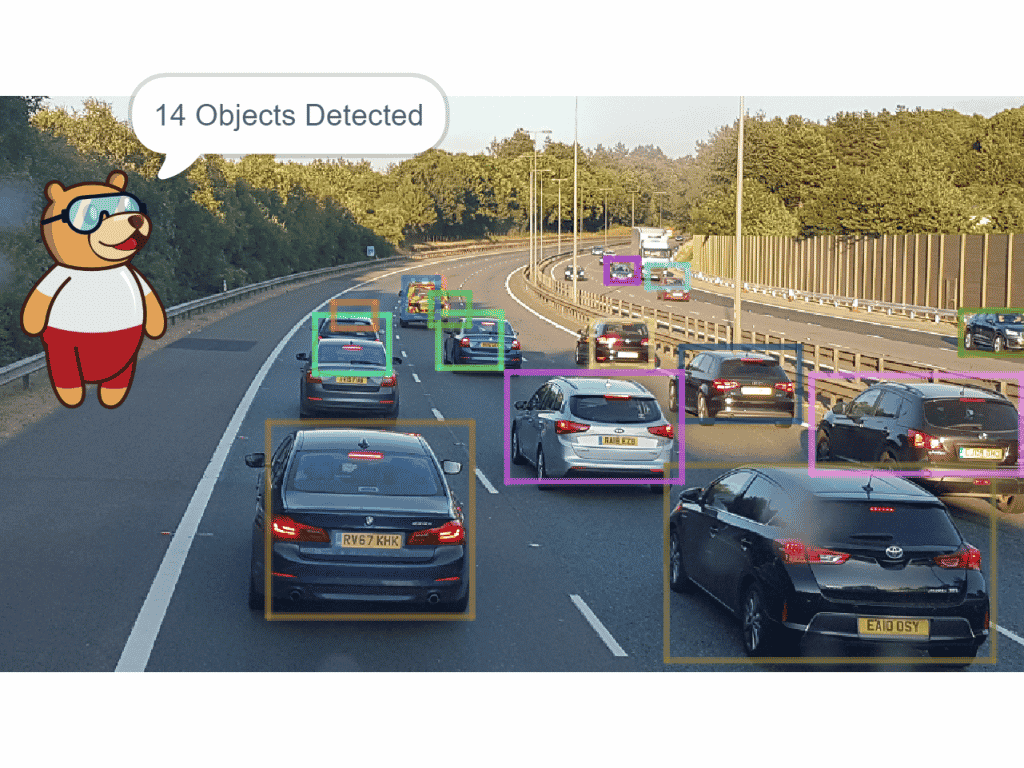

One of the applications of Object detection includes Self-driving vehicles which detect objects in real-time and act accordingly.
![]() The object detection extension in PictoBlox allows you to detect the following 90 objects:
The object detection extension in PictoBlox allows you to detect the following 90 objects:
| ID | OBJECT (PAPER) | SUPER CATEGORY |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | person | person |
| 2 | bicycle | vehicle |
| 3 | car | vehicle |
| 4 | motorcycle | vehicle |
| 5 | airplane | vehicle |
| 6 | bus | vehicle |
| 7 | train | vehicle |
| 8 | truck | vehicle |
| 9 | boat | vehicle |
| 10 | traffic light | outdoor |
| 11 | fire hydrant | outdoor |
| 12 | street sign | outdoor |
| 13 | stop sign | outdoor |
| 14 | parking meter | outdoor |
| 15 | bench | outdoor |
| 16 | bird | animal |
| 17 | cat | animal |
| 18 | dog | animal |
| 19 | horse | animal |
| 20 | sheep | animal |
| 21 | cow | animal |
| 22 | elephant | animal |
| 23 | bear | animal |
| 24 | zebra | animal |
| 25 | giraffe | animal |
| 26 | hat | accessory |
| 27 | backpack | accessory |
| 28 | umbrella | accessory |
| 29 | shoe | accessory |
| 30 | eye glasses | accessory |
| 31 | handbag | accessory |
| 32 | tie | accessory |
| 33 | suitcase | accessory |
| 34 | frisbee | sports |
| 35 | skis | sports |
| 36 | snowboard | sports |
| 37 | sports ball | sports |
| 38 | kite | sports |
| 39 | baseball bat | sports |
| 40 | baseball glove | sports |
| 41 | skateboard | sports |
| 42 | surfboard | sports |
| 43 | tennis racket | sports |
| 44 | bottle | kitchen |
| 45 | plate | kitchen |
| 46 | wine glass | kitchen |
| 47 | cup | kitchen |
| 48 | fork | kitchen |
| 49 | knife | kitchen |
| 50 | spoon | kitchen |
| 51 | bowl | kitchen |
| 52 | banana | food |
| 53 | apple | food |
| 54 | sandwich | food |
| 55 | orange | food |
| 56 | broccoli | food |
| 57 | carrot | food |
| 58 | hot dog | food |
| 59 | pizza | food |
| 60 | donut | food |
| 61 | cake | food |
| 62 | chair | furniture |
| 63 | couch | furniture |
| 64 | potted plant | furniture |
| 65 | bed | furniture |
| 66 | mirror | furniture |
| 67 | dining table | furniture |
| 68 | window | furniture |
| 69 | desk | furniture |
| 70 | toilet | furniture |
| 71 | door | furniture |
| 72 | tv | electronic |
| 73 | laptop | electronic |
| 74 | mouse | electronic |
| 75 | remote | electronic |
| 76 | keyboard | electronic |
| 77 | cell phone | electronic |
| 78 | microwave | appliance |
| 79 | oven | appliance |
| 80 | toaster | appliance |
| 81 | sink | appliance |
| 82 | refrigerator | appliance |
| 83 | blender | appliance |
| 84 | book | indoor |
| 85 | clock | indoor |
| 86 | vase | indoor |
| 87 | scissors | indoor |
| 88 | teddy bear | indoor |
| 89 | hair drier | indoor |
| 90 | toothbrush | indoor |
| 91 | hair brush | indoor |
Accessing Object Detection in Block Coding
Following is the process to add Object Detection capability to the PictoBlox Project.
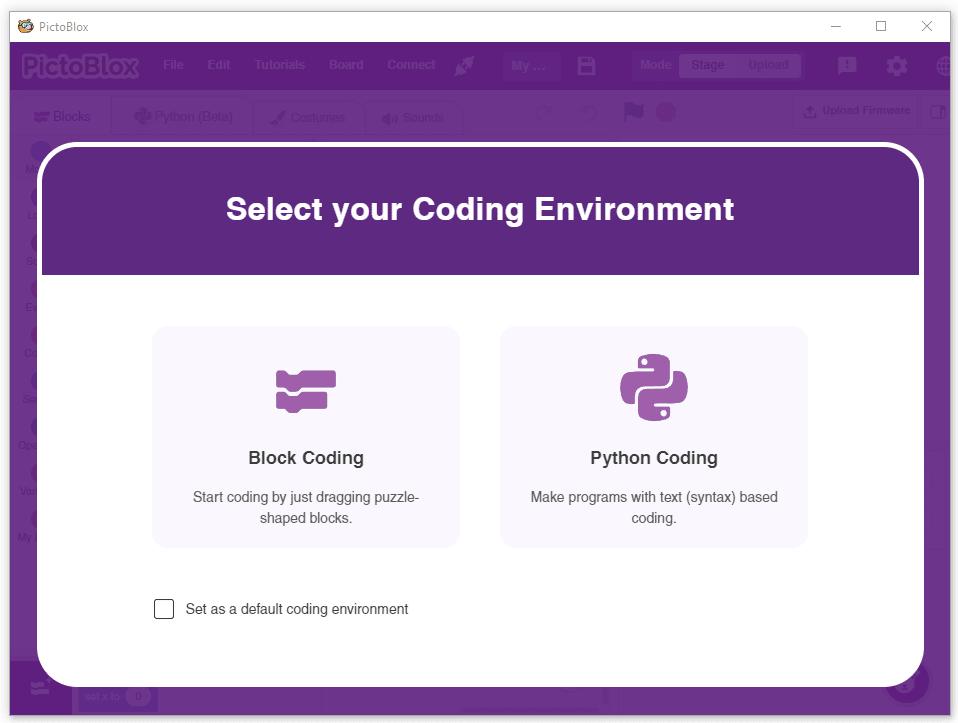
- Open PictoBlox and create a new file.

- Select the coding environment as appropriate Coding Environment.
- Next, click on the Add Extension button and add the Object Detection extension.
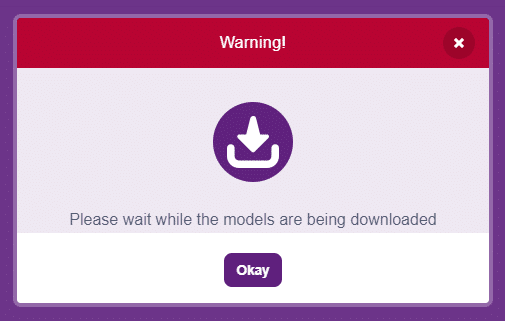
- The object detection models will be downloaded, which may take a few seconds to load.
- Once downloaded you will get a message saying “Model loaded successfully”.
- You can find the object detection blocks available in the project.
Accessing Object Detection in Python Coding
Following is the process to add Object Detection capability to the PictoBlox Project.
- Open PictoBlox and create a new file.
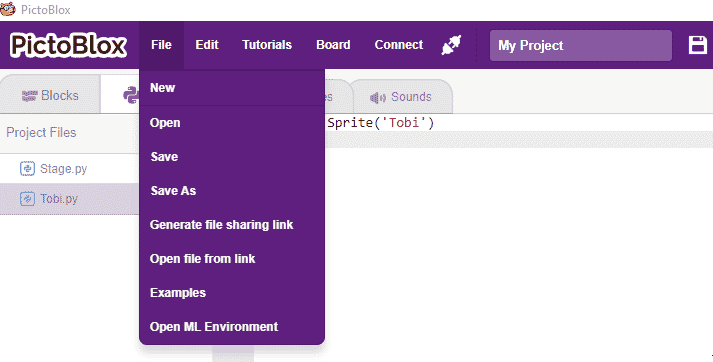
- Select the coding environment as Block Coding.

- Next, click on the Add Modules/Libraries button and add the Face Detection extension.

- To access the library functions, you have to add the object declaration.
od = ObjectDetection()