Natural Language Processing

-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode
Mode: Stage Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA, None
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA, None
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky, None
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky, None
-
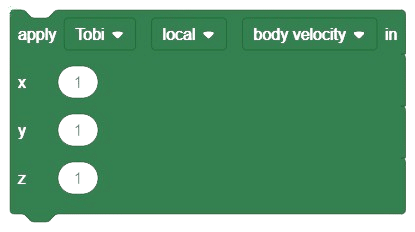
 Object Declaration in Python: nlp = NaturalLanguageProcessing()
Object Declaration in Python: nlp = NaturalLanguageProcessing()
-
 Extension Catergory: Artificial Intelligence
Extension Catergory: Artificial Intelligence
Introduction
Natural Language Processing, abbreviated as NLP, is a branch of artificial intelligence that deals with the interaction between computers and humans using natural language. Natural language refers to language that is spoken and written by people, and natural language processing (NLP) attempts to extract information from the spoken and written word using algorithms.
The ultimate objective of NLP is to read, decipher, understand, and make sense of human languages in a manner that is valuable.
NLP in PictoBlox
To make the text classifier, we have the Natural Language Processing extension.
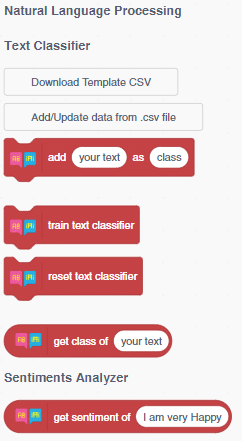
Application
- Email Filters: Email filters are one of the most basic and initial applications of NLP online. It started out with spam filters, uncovering certain words or phrases that signal a spam message.

- Smart Assistants: Smart assistants like Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa recognize patterns in speech, then infer meaning and provide a useful response.

Accessing NLP in Block Coding
Following is the process to add Natural Language Processing capability to the PictoBlox Project.
- Open PictoBlox and create a new file.

- Select the coding environment as Block Coding.
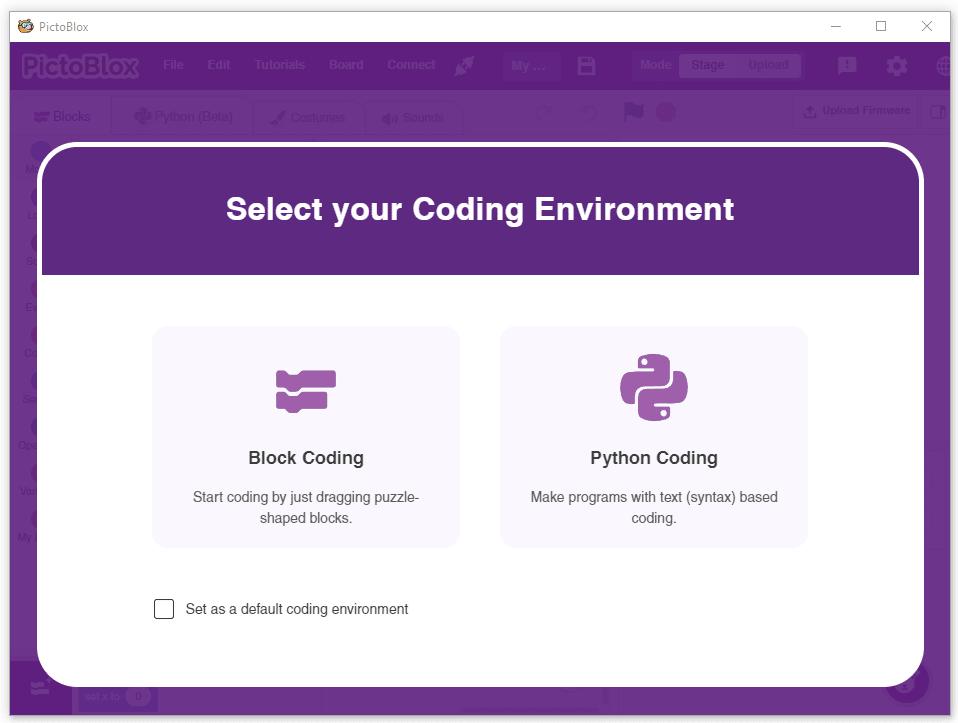
- Next, click on the Add Extension button and add the Natural Language Processing extension.

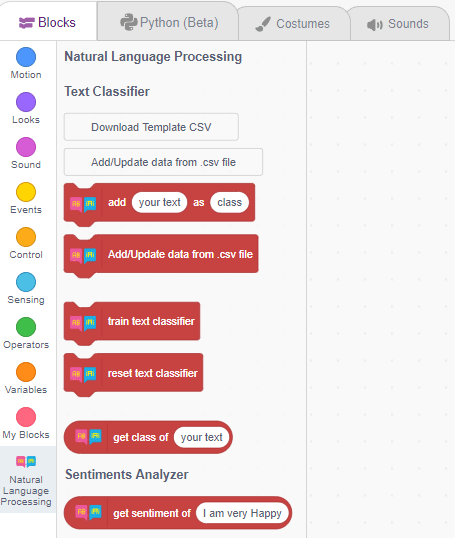
- You can find the Natural Language Processing blocks available in the project.
Accessing NLP in Python Coding
Following is the process to add Natural Language Processing capability to the PictoBlox Project.
- Open PictoBlox and create a new file.
- Select the coding environment as Python Coding.

- Next, click on the Add Modules/Libraries button and add the Natural Language Processing extension.

- To access the library functions, you have to add the object declaration.
nlp = NaturalLanguageProcessing()