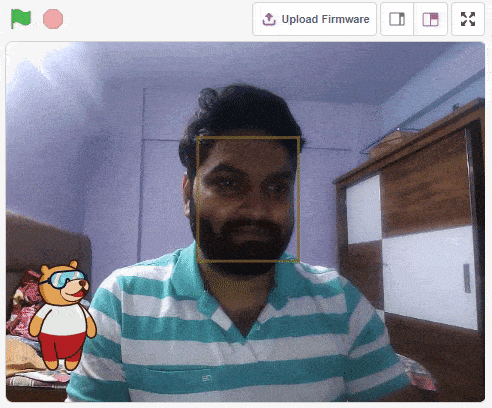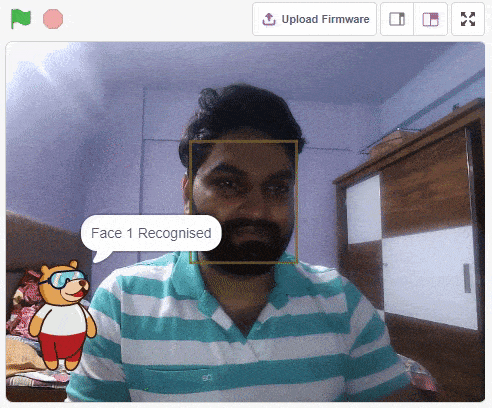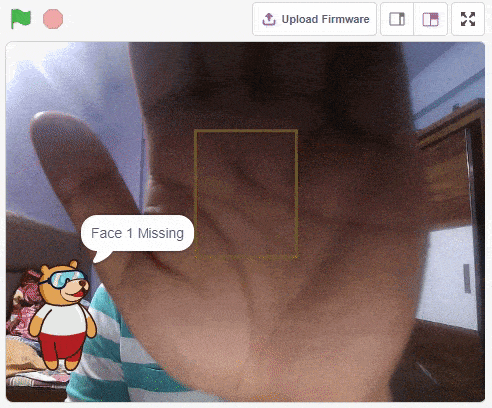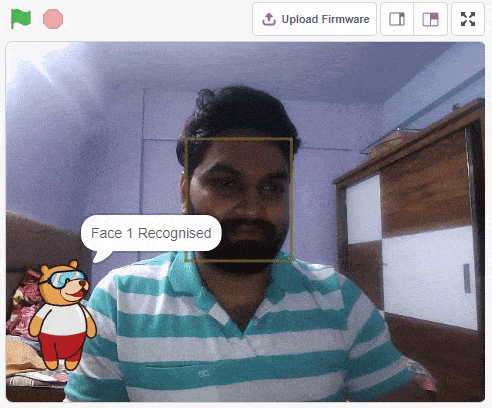
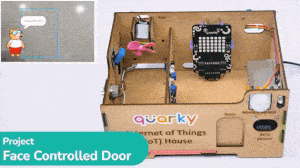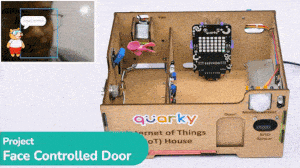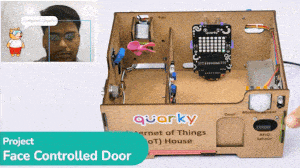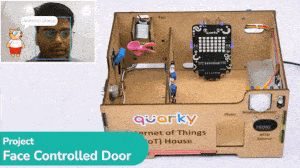
IoT House (Quarky)
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
Mode: Stage Mode, Upload Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: Quarky
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
Compatible Hardware in Python: Quarky
-
 Object Declaration in Python: Not Applicable
Object Declaration in Python: Not Applicable
-
 Extension Catergory: Quarky
Extension Catergory: Quarky
Introduction
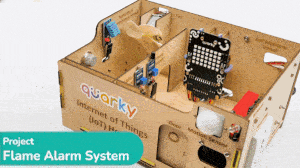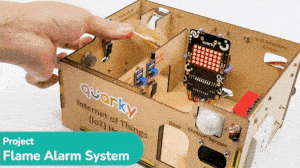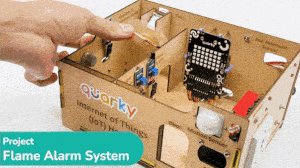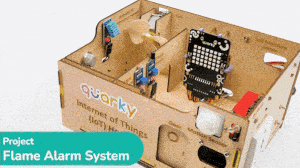
The IoT House kit is perfect for those looking to explore the Internet of Things world. With 15+ activities, this kit will guide you through the basics of IoT and help you better understand how these systems work.
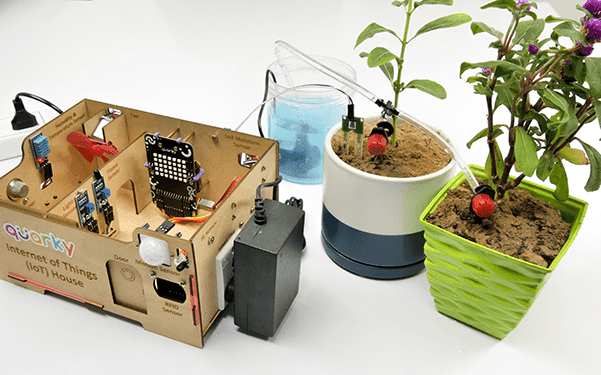
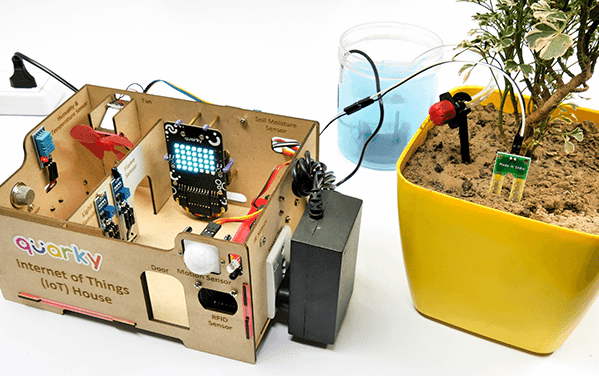
The Quarky IoT House kit has the following sensors/actuators:
- Motor with Fan
- Flame Sensor
- Infrared Distance Sensor
- Gas Sensor
- Humidity and Temperature Sensor
- Light Sensor
- Soil Moisture Sensor
- Motion Sensor
- RFID Sensor
- Servo Motor for Door Operation
- Relay module
Links for Assembly Instructions
You can follow the tutorials to assemble the IoT house and drip irrigation:
- IoT House – Assembly Guide: This tutorial will guide us through assembling the IoT House for Quarky.

- 1 Plant Drip Irrigation Assembly: This tutorial will show you how to put together the Quarky IoT House Addon kit to make a 1 plant drip irrigation system.
- 2 Plants Drip Irrigation Assembly: In this tutorial, you will be provided with instructions on how to use the Quarky IoT House Addon kit to assemble a drip irrigation system for two plants.

Python Object Declaration for Stage Mode
Stage mode is one of the two modes you can write your programs in Pictoblox. In this mode, you can write scripts for the sprite and boards to interact with sprites in real time. If you disconnect the board with Pictoblox, you cannot interact with the board anymore. In this mode, you can make games and animations interacting with Quarky.
You can toggle between the upload mode and stage mode using the button on the top right side of Pictoblox.

In Python Coding Environment, use the following object declaration to use Python functions in Stage Mode:
iothouse = IoTHouse()Upload Mode
Upload mode is one of the two modes you can write your programs in Pictoblox. This mode allows you to write scripts and upload them to the board so that you can use them even when it is not connected to your computer, for example, you need to upload a script for making moving robots.
In this case, Quarky will run offline according to the program and it can not interact with the stage.
In Python Coding Environment, use the following object declaration to use Python functions in Upload Mode:
import iothouse