3D and XR Studio Transform
-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode
Mode: Stage Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
Compatible Hardware in Python: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
-
 Object Declaration in Python: .
Object Declaration in Python: .
-
 Extension Catergory: 3D and XR Studio
Extension Catergory: 3D and XR Studio
Introduction
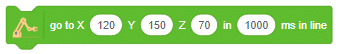
Transform provides users with an interface to manipulate layers:
1. Position, Scale, Rotation:
– Position: Users can precisely define the location of layers within their scenes, ensuring objects are placed exactly where they want them. This capability is essential for arranging elements in a scene to achieve desired compositions or layouts.
– Scale: Scaling allows users to adjust the size of layers, either uniformly or along specific axes. This flexibility enables them to create objects of varying sizes and proportions, enhancing visual diversity and realism in their scenes.
– Rotation: Users can specify the orientation of layers in three-dimensional space, controlling their tilt, angle, and orientation relative to the scene’s coordinate system. Rotation adds depth and dynamism to scenes, allowing users to create immersive environments and unique visual perspectives.
2. Animation Integration:
– Custom Animations: Platform provides users with a library of pre-defined animations that can be easily applied to layers. These animations cover common motions such as scaling, rotation, and more, allowing users to quickly add movement and interactivity to their scenes without the need for extensive scripting or programming.
– In-built Animations: User can also use the inbuilt animation created while creation of the 3D objects.