PictoBlox also provides the ability to program the Quarky Mecanum using Python in Desktop / Laptop versions. Let’s see how you can do it in this lesson.
PictoBlox
With PictoBlox, you can program the Quarky Mecanum!
If you haven’t installed PictoBlox, please follow the instructions:
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_wrapper_link" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/wrapper-link.php on line 194
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_wrapper_link_enable" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/wrapper-link.php on line 196
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_icon" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 350
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_text" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 351
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_target" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 352
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_css_selector" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 353
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_enable" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 355
Connecting Quarky with PictoBlox
Let’s begin by first connecting Quarky to PictoBlox. Follow the steps below for connecting Quarky to PictoBlox:
-
- First, connect Quarky to your laptop using a USB cable.
- Next, open PictoBlox on your desktop.
- After that, select Python Coding as your coding environment.
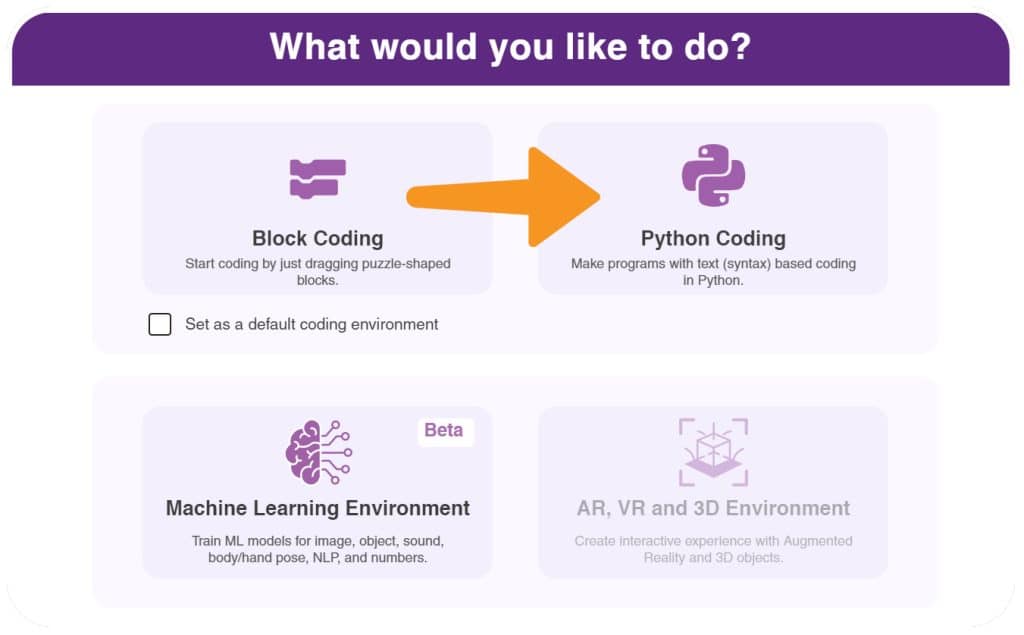
- Then, click the Board button in the toolbar and select Board as Quarky.
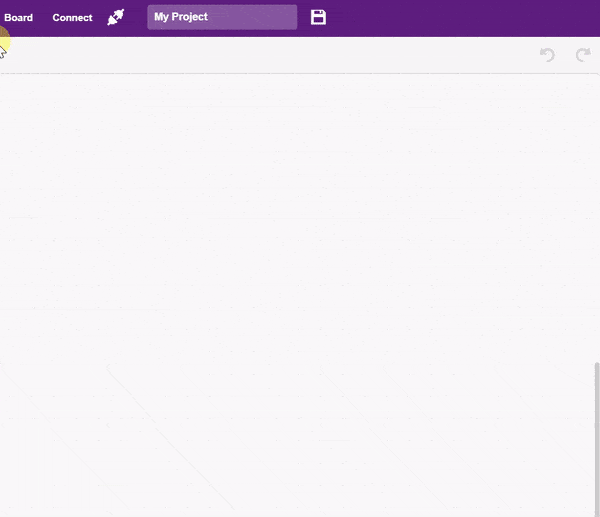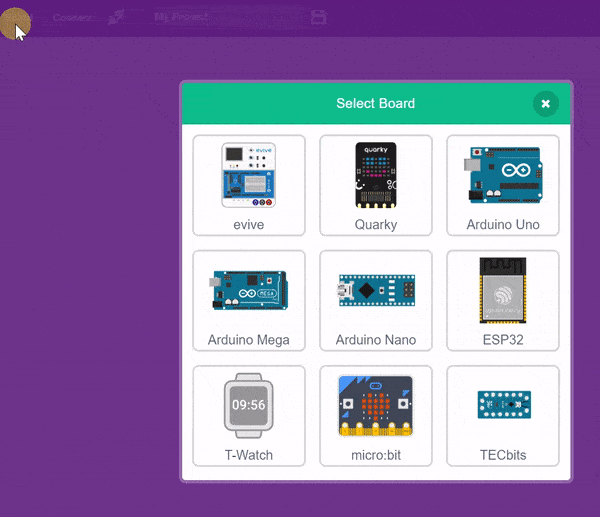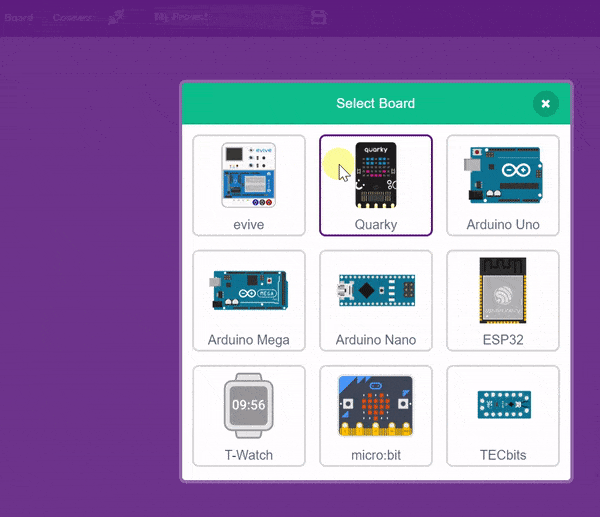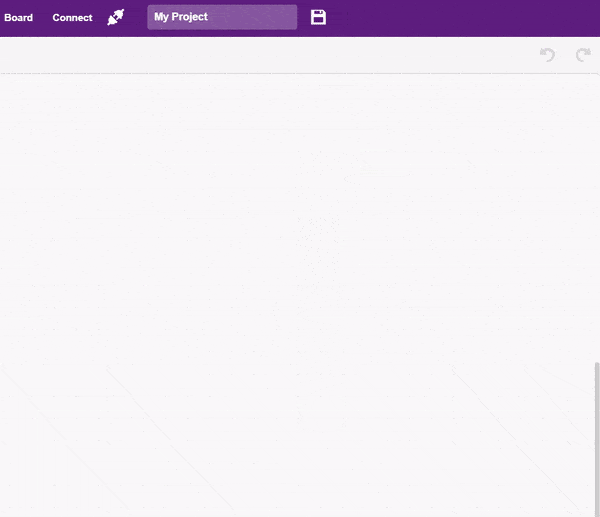
- Next, select the appropriate Serial port if the Quarky is connected via USB or the Bluetooth Port if you want to connect Quarky via Bluetooth and press Connect.
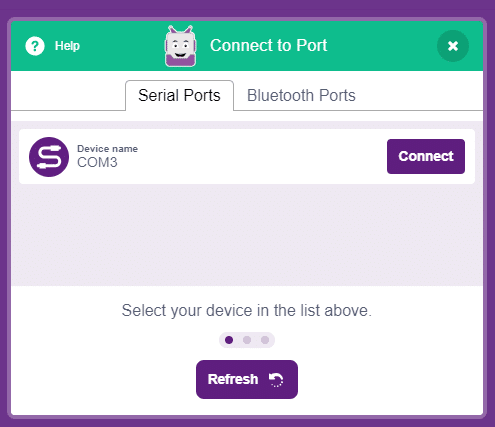
- Click on the Upload Firmware button. This will upload the latest firmware in Quarky.
 Note: If your device already has the latest firmware, then PictoBlox will show the message – Firmware is already updated. For learning more you can refer to this tutorial: https://ai.thestempedia.com/docs/quarky/quarky-toubleshooting/updating-quarky-firmaware-with-pictoblox/
Note: If your device already has the latest firmware, then PictoBlox will show the message – Firmware is already updated. For learning more you can refer to this tutorial: https://ai.thestempedia.com/docs/quarky/quarky-toubleshooting/updating-quarky-firmaware-with-pictoblox/ - Once the firmware is uploaded, Quarky starts the Getting Started program. This runs only for the first time. Run through it.
And voila! Quarky is now connected to PictoBlox.
Quarky Mecanum Python Library for Stage Mode
Stage mode is one of the two modes you can write your programs in PictoBlox. In this mode, you can write scripts for the sprite and boards to interact with sprites in real-time. If you disconnect the board with PictoBlox, you cannot interact with the board anymore.
You can toggle between the upload mode and stage mode using the button on the top right side of PictoBlox.
In Python, use the following object declaration to use Python functions in Stage Mode:
meca = Mecanum(1, 2, 7, 8)Quarky Mecanum Python Library for Upload Mode
Upload mode allows you to write scripts and upload them to the board so that you can use them even when it is not connected to your computer, for example, you need to upload a script for making moving robots. In this case, Quarky will run offline according to the program and it cannot interact with the stage.
In Python, use the following object declaration to use Python functions in Upload Mode:
from quarky import *
from expansion_addon import Mecanum
meca = Mecanum(1, 2, 7, 8)Python Functions
The following functions are available for use in the Quarky Mecanum library:
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_wrapper_link" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/wrapper-link.php on line 194
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_wrapper_link_enable" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/wrapper-link.php on line 196
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_icon" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 350
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_text" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 351
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_target" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 352
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_css_selector" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 353
Warning: Undefined array key "pp_custom_cursor_enable" in /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/powerpack-elements/extensions/custom-cursor.php on line 355
Conclusion
In conclusion, PictoBlox is a powerful coding environment that allows you to program the Quarky Mecanum Robot with Python in both Stage and Upload modes. The Quarky Mecanum library provides several functions that can be used to control the robot’s motors, pick–and–place robot, and gripper robot. With the help of PictoBlox, you can easily program and control the Quarky Mecanum robot!